| Lesson 2 | Recovery Manager Features |
| Objective | Identify Features and Enhancements for Oracle's Recovery Manager (RMAN). |
Oracle Recovery Manager Features
Identify Features and enhancements for Oracle's Recovery Manager (RMAN). Data backups are critical to database recovery. However, very large database systems impose stringent requirements for backup and recovery operations. In many cases, the physical action of copying the database files can take several hours, due to the large size and number of files. In addition, backup and recovery operations must be performed with minimal interruption to business processing.
RMAN can back up without closing Database
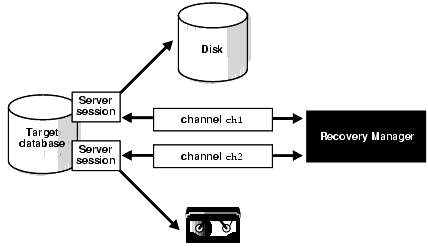
The RMAN provides an integrated method for creating, managing, and restoring database backups. RMAN provides greater ease of management and administration for the backup and recovery operations, while maintaining superior performance, and increased availability of the database. RMAN can perform a full or incremental back up of an entire database, or a subset, while the database is open or closed.
Automatic multiplexing
In addition, Oracle now provides tighter integration within a cluster environment, so that even if one of the cluster nodes fail,
the processes and transactions associated with the failed node are transferred to another node. This also helps balance the load of processes and users that are connected to the database.
RMAN utilizes knowledge of file affinity to back up data efficiently within a distributed storage environment. In addition, RMAN can automatically multiplex backups to protect data from backup media failures.
A summary of the new Oracle RMAN functionality includes:
- File affinity: The export file created has the role and responsibility of the user within it and when the file is imported by another user, this user must have the same set of roles and responsibility to complete an import.
- Proxy copy: A proxy copy is a special type of backup, in which RMAN turns over control of the data transfer to a media manager that supports this feature. The PROXY option of the BACKUP command specifies that a backup should be a proxy copy.
- Disk affinity: An OPS instance is said to have affinity for a device if the device is directly accessible from the node on which the instance is running
LISTcommand enhancements- Recovery catalog cross checks
- Multiplexed backup sets: The technique of RMAN multiplexing is to simultaneously read files on disks and and then write them into the same backup piece.
- Control file character set specification
STARTUPandSHUTDOWNcommands- Clone command
- Automatic catalog maintenance
GUI or command line
RMAN is available in two modes, Graphic User Interface (GUI) and command line mode. The GUI mode can be accessed only through the Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM). The GUI is available as a wizard to assist the user in backup or recovery of a database through five steps. The command line mode is accessible by typing RMAN at the O/S prompt. RMAN allows you to create backup and recovery scripts and execute or schedule them by using OEM. The following contains more information regarding Oracle
application development tools
The next lesson is about the new backup strategies available in Oracle.
The next lesson is about the new backup strategies available in Oracle.
