| Lesson 8 | Transparent application failover |
| Objective | Describe how to set up TAF |
Transparent Application Failover (TAF) still exists in Oracle Database 23c.
Oracle's documentation for 23c continues to describe TAF as a client-side high-availability feature. It enables client applications, such as those using ODP.NET or JDBC, to automatically reconnect to a secondary database instance if the primary instance fails. This reconnection process is designed to be transparent to the application, minimizing disruption. TAF supports different failover types, such as `SELECT` (re-executing queries) and `SESSION` (re-establishing the session, requiring transactions to be restarted).
While TAF is still available, Oracle has also been heavily promoting Application Continuity (AC) and Transparent Application Continuity (TAC). These are more advanced features that aim to provide an even more seamless failover experience by not only reconnecting the session but also by attempting to recover the transactional and session state, and replay in-flight operations. In many modern Oracle discussions and recommendations for high availability, Application Continuity is often highlighted as the preferred and more comprehensive solution for masking database outages from end-users and applications. In summary:
While TAF is still available, Oracle has also been heavily promoting Application Continuity (AC) and Transparent Application Continuity (TAC). These are more advanced features that aim to provide an even more seamless failover experience by not only reconnecting the session but also by attempting to recover the transactional and session state, and replay in-flight operations. In many modern Oracle discussions and recommendations for high availability, Application Continuity is often highlighted as the preferred and more comprehensive solution for masking database outages from end-users and applications. In summary:
- TAF is still a feature in Oracle 23c.
- Application Continuity (AC) and Transparent Application Continuity (TAC) are more advanced and often recommended Oracle features for achieving application high availability and transparent failover with state recovery.
Transparent Application Failover
Transparent application failover (TAF):
A feature in Net8 to seamlessly move a user’s session from one instance to another when the original instance fails.
Transparent application failover (TAF) ensures that in-progress transactions can be immediately resumed whenever an Oracle database instance becomes unavailable due to a lost network connection.
TAF can hide the connection failures from end-users, and preserve the existing state of their applications when the connection has failed. TAF also provides the ability to resume queries that were in progress at the time of the failure. TAF automatically logs a user in with the same user ID as was used prior to failure. If multiple users were using the connection, TAF automatically logs them in as they attempt to process database commands. Unfortunately, TAF cannot automatically restore other session properties. Look at the following MouseOver to see the configuration of the tnsnames.ora file needed to implement TAF.
TAF can hide the connection failures from end-users, and preserve the existing state of their applications when the connection has failed. TAF also provides the ability to resume queries that were in progress at the time of the failure. TAF automatically logs a user in with the same user ID as was used prior to failure. If multiple users were using the connection, TAF automatically logs them in as they attempt to process database commands. Unfortunately, TAF cannot automatically restore other session properties. Look at the following MouseOver to see the configuration of the tnsnames.ora file needed to implement TAF.
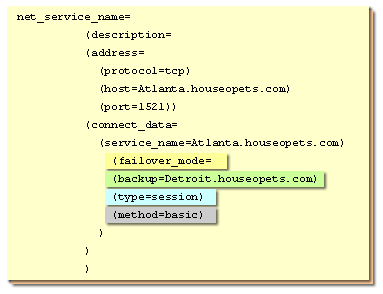
- This parameter indicates that you are going to use TAF. If you leave out this parameter, or set the TYPE sub-parameter to NONE, no failovers are handled.
- Name the database service that picks up the failed transaction.
- Specify which type of failover you wish to handle. The choices are: SESSION (a user session failure is reconnected on the backup.); SELECT (a user's cached query continues to deliver data after instance failure); and NONE (no failovers allowed).
- Specify the method used for failover. The chouces are: BASIC (creates a connection on the backup only when a failure occurs.); PRECONNECT (creates a connection on the backup during normal sessions so failover - if needed - is faster.)
Configuring Transparent Application failover
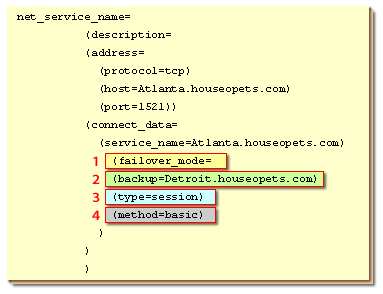
| Hotspot 1 | This parameter indicates that you are going to use TAF. If you leave out this parameter, or set the TYPE sub-parameter to NONE, no failoversare handled. |
| Hotspot 2 | Name the database service that picks up the failed transaction. |
| Hotspot 3 | Specify which type of failover you wish to handle. The choices are: SESSION (a user session failure is reconnected on the backup.); SELECT (a user's cached query continues to deliver data after instance failure); and NONE (no failovers allowed). |
| Hotspot 4 | Specify the method used for failover. The chouces are: BASIC (creates a connection on the backup only when a failure occurs.); PRECONNECT (creates a connection on the backup during normal sessions so failover - if needed - is faster.) |
The SELECT type of failover requires storage of query results on the client side, where the SESSION type of failover requires no client side activity. The next lesson wraps up the module.
Transparent Application Failover - Exercise
Click the Exercise link below to put lines in the tnsnames.ora file in the proper order.
Transparent Application Failover - Exercise
Transparent Application Failover - Exercise