| Lesson 7 | Date and time functions for Date manipulation |
| Objective | Identify valid date-related functions and Oracle's standard date format. |
Oracle Date and Time Functions
This lesson looks at a few of the more commonly used date functions that work with the "date portion" of the "date datatype". Since the date datatype also contains time, the next lesson illustrates functions you can use to manipulate the time portion of a date.
- Date Functions: The default display format for dates in Oracle is: DD-MON-YY. However, dates are actually stored in the database as a large number that facilitates date comparisons and date arithmetic. There are many functions for manipulating dates. The following table lists them all.
| Function | Syntax | Description |
ADD_MONTHS | ADD_MONTHS(col1, n) | Add n months to col1 |
LAST_DAY | LAST_DAY(col1) | Date of the last day of the month for col1 |
MONTHS_BETWEEN | MONTHS_BETWEEN(col1, col2) | Number of months between two dates. Returns fraction of month if days of the two dates are different. |
NEW_TIME | NEW_TIME(col1, zone1, zone2) | Converts date and time from zone1 to zone2 |
NEXT_DAY | NEXT_DAY(col1, day) | Returns the date of the next day named by day (such as 'MONDAY') |
ROUND | ROUND(col1,[round_to]) | Returns the date rounded to the nearest day by default; can round to nearest month, quarter, year, hour, and so on based on round_to format |
TRUNC | TRUNC(col1, [trunc_to]) | Returns the date with the time removed; can truncate to nearest month, quarter, year, hour, and so on based on trunc_to format |
TO_CHAR | TO_CHAR(col1, date_format) | Returns date and/or time based on format listed |
Modern Date Formatting
While TO_CHAR is still available and functional in Oracle, it's important to understand its role in the larger context of date formatting:
Current Best Practices:
When to use TO_CHAR:
Current Best Practices:
- Use built-in date formatting options: Modern versions of Oracle (12c and later) offer improved formatting options directly within date-related functions like `TO_DATE` and `TO_TIMESTAMP`. These offer a wider range of pre-defined formats and more flexibility compared to `TO_CHAR`.
- Consider the `NLS_DATE_FORMAT` parameter: This session-level parameter sets the default date format used by various date functions, including `TO_CHAR`. It often aligns with the user's locale settings, providing consistency.
- Explore alternatives for specific needs: For complex formatting or internationalization requirements, other options like Oracle Globalization Support (NLS) and third-party tools might be more suitable.
When to use TO_CHAR:
- Backward compatibility: If you're working with old code or scripts relying on `TO_CHAR`, it's still functional.
- Specific formatting not available otherwise: If you need a format not offered by other functions, `TO_CHAR` might be necessary.
- `TO_CHAR` remains functional in Oracle but "not generally recommended" as the first choice for date formatting.
- Modern alternatives offer more flexibility and alignment with current standards.
- Use `TO_CHAR` judiciously, prioritizing newer options whenever possible.
TO_CHAR Function
You can display an Oracle date as any of dozens of format combinations. Just use this basic layout:
The format parameter is always enclosed in single quotes and uses symbols defining how the date is displayed. Here are some of the date format symbols:
There are many more, but these are the major ones. The following series of images shows several examples of the
TO_CHAR(col1,'format')The format parameter is always enclosed in single quotes and uses symbols defining how the date is displayed. Here are some of the date format symbols:
| Format parameter | Description |
MM | Month in numbers (01 - 12) |
Month | Month spelled out with initial capital letter (January - December) |
MONTH | Month spelled in all capital letters (JANUARY - DECEMBER) |
MON | Three character abbreviation of month in capital letters (JAN - DEC) |
DD | Day in numbers (01 - 31) |
DDth | 01st, 02nd, and so on |
DDD | number of day in the year (1 - 366) |
Day | Day spelled out with initial capital letter (Monday - Sunday) |
DAY | Day of week in all capital letters (MONDAY - SUNDAY) |
YY | Last two digits of year (00 - 99) |
Year | Year spelled out with initial capital (such as Two Thousand) |
RR | Rounded year; if year is <50, it will round up to the next century if current year is > 50. |
HH or HH12 | Hour (1 - 12) |
HH24 | Hour (0 - 23) |
MI | Minutes (00 - 59) |
PM | Meridian in capital letters (AM or PM) |
P.M. | Meridian (A.M. or P.M.) |
| SS | Seconds (00 - 59) |
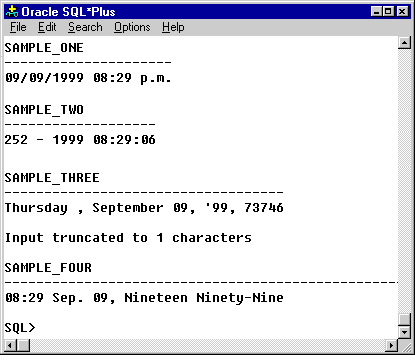
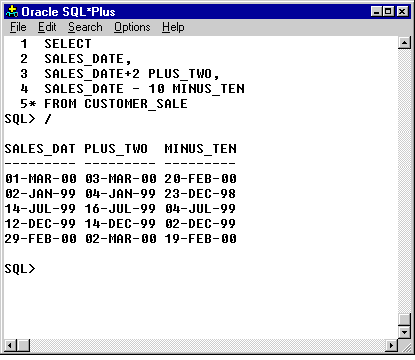
There are many more, but these are the major ones. The following series of images shows several examples of the
TO_CHAR() function with a variety of date formats, plus some date arithmetic.
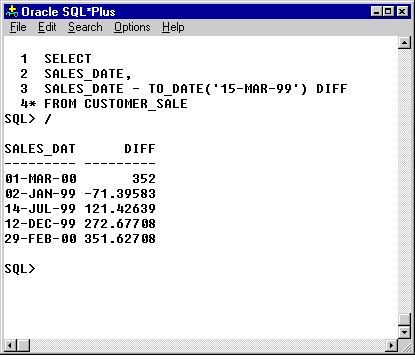
SELECT
SALES_DATE,
SALES_DATE - TO_DATE('15-MAR-99') DIFF
* FROM CUSTOMER_SALE
When adding or subtracting years and months, you get different behavior from using ADD_MONTHS, which operates on values of type DATE, than from using interval arithmetic on the timestamp types.
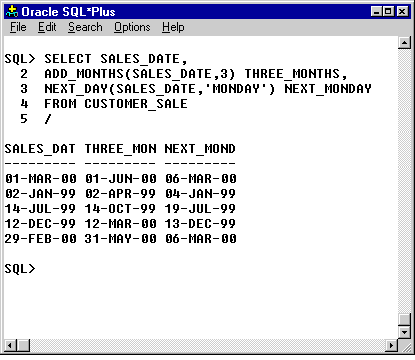
SELECT SALES_DATE, ADD_MONTHS(SALES_DATE,3) THREE_MONTHS, NEXT_DAY(SALES_DATE, 'MONDAY') NEXT_MONDAY FROM CUSTOMER_SALE
Oracle Date formats and date Arithmetic
A format model is a character literal that describes the format of datetime or numeric data stored in a character string. A format model does not change the internal representation of the value in the database. When you convert a character string into a date or number, a format model determines how Oracle Database interprets the string. In SQL statements, you can use a format model as an argument of the TO_CHAR and TO_DATE functions to specify:
- The format for Oracle to use to return a value from the database
- The format for a value you have specified for Oracle to store in the database
- The datetime format model for the string '17:45:29' is 'HH24:MI:SS'.
- The datetime format model for the string '11-Nov-1999' is 'DD-Mon-YYYY'.
- The number format model for the string '$2,304.25' is '$9,999.99'.
ADD_MONTHS
The ADD_MONTHS function returns the date resulting from date plus integer months.
SQL syntax
Description
The Oracle date has always contained all four digits of the year. Even when your input only requires two digits entered for the year, Oracle adds in the century before storing the date in the database.
ADD_MONTHS (Date,Integer)Parameters: ADD_MONTHS has the parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
| Date | A datetime value or any value that can be converted to a datetime value. |
| Integer | An integer or any value that can be converted to an integer. |
Description
- The return type is always DATE regardless of the data type of date. Supported data types are DATE, TIMESTAMP, ORA_TIMESTAMP and ORA_DATE.
- Data types TIME, TT_TIME, TT_DATE and TT_TIMESTAMP are not supported.
- If date is the last day of the month or if the resulting month has fewer days than the day component of date, then the result is the last day of the resulting month. Otherwise, the result has the same day component as date.
The Oracle date has always contained all four digits of the year. Even when your input only requires two digits entered for the year, Oracle adds in the century before storing the date in the database.
Ad Oracle Database SQL
Oracle Date/time functions for Date Manipulation
If you use a two-digit year as input, Oracle assigns the current century to the date. This became a problem in the year 1999, as programmers prepared their systems for the year 2000. As a result, Oracle created a new date format:
Oracle 19c can use the RR format as a rounding Function
While the `RR` format in Oracle 19c still exists and behaves similarly to how it did in previous versions, it's important to understand its exact function and potential caveats: The `RR` format element can still be used for rounding two-digit years. However, it's essential to remember that it primarily acts as an "input format",
meaning it interprets a two-digit year based on the current year within the context of the century. It doesn't round a stored date value.
Here's a breakdown of its behavior:
For example, today's date is February 17, 2024 (Year: 2024, Last two digits: 24).
Therefore, while `RR` can be used for certain input scenarios, it's generally recommended to "use explicit four-digit years" for dates whenever possible to avoid ambiguity and ensure consistent interpretation across different times. This is especially important for storing dates in the database.
Here's a breakdown of its behavior:
- When you provide a two-digit year using `RR`, it interprets it based on the first 2 digits of the current year.
- If the last two digits of the current year are 00 to 49, the first 2 digits of the interpreted year will be 1 less than the current year's first 2 digits.
- If the last two digits of the current year are 50 to 99, the interpreted year will have the same first 2 digits as the current year.
For example, today's date is February 17, 2024 (Year: 2024, Last two digits: 24).
- If you enter `01-JAN-40` with `RR` format, it interprets the year as 2040 (2024-1+40).
- If you enter `01-JAN-80` with `RR` format, it interprets the year as 2080 (same first 2 digits as 2024).
- Data storage: If you store a date with `RR`, it will store the exact two-digit year you entered, not the interpreted year. Rounding only happens during input interpretation.
- Potential ambiguity: Using `RR` can lead to ambiguity in the future, especially when the current year changes to a different first 2 digits. Dates stored with `RR` might be interpreted differently depending on the current year at that time.
Therefore, while `RR` can be used for certain input scenarios, it's generally recommended to "use explicit four-digit years" for dates whenever possible to avoid ambiguity and ensure consistent interpretation across different times. This is especially important for storing dates in the database.
The
RR format is a rounding function for two-digit years that allows you to input a two-digit year and have it adjusted to the correct century, for most applications. So long as the last two digits of the current year are between 00 and 49, the RR format assigns the current century to all two-digit dates between 00 and 49 that are inserted or updated into the database. For incoming dates between 50 and 99, the previous century is assigned. When the last two digits of the current year are between 50 and 99, the RR format assigns the next century to all incoming dates with two-digit years between 00 and 49. For incoming dates between 50 and 99, the current century gets assigned. Of course, you can always input a four-digit year and have it loaded exactly as you type it into the database.
Date Arithmetic
DATE is an Oracle datatype, just as VARCHAR2 and NUMBER are, and it has its own unique properties. The DATE datatype is stored in a special internal Oracle format that includes not just the
- month,
- day, and
- year,
SQL*Plus
and SQL recognize columns that are of the DATE datatype, and they understand that instructions to do arithmetic with them call for date arithmetic, not regular math. Adding 1 to a date, for instance, will give you another date, which is the next day. Subtracting one date from another will give you a number which is the count of days between the two dates. However, because Oracle dates can include
- hours,
- minutes, and
- seconds,
Oracle SYSDATE, CURRENT_DATE, and SYSTIMESTAMP
Oracle taps into the operating system of the computer for the current date and time. It makes these available to you through a special function called SYSDATE. Think of SYSDATE as a function whose result is always the current date and time, and it can be used wherever any other Oracle function can be used. You also can regard it as a hidden column or pseudo-column that is in every table.
Here, SYSDATE shows the date of today:
In the next lesson, you will learn how to identify valid time-related date/time functions.
select SysDate from DUAL; SYSDATE --------- 28-FEB-08Note: DUAL is a small but useful Oracle table created for testing functions or doing quick calculations.
In the next lesson, you will learn how to identify valid time-related date/time functions.