OEM Architecture
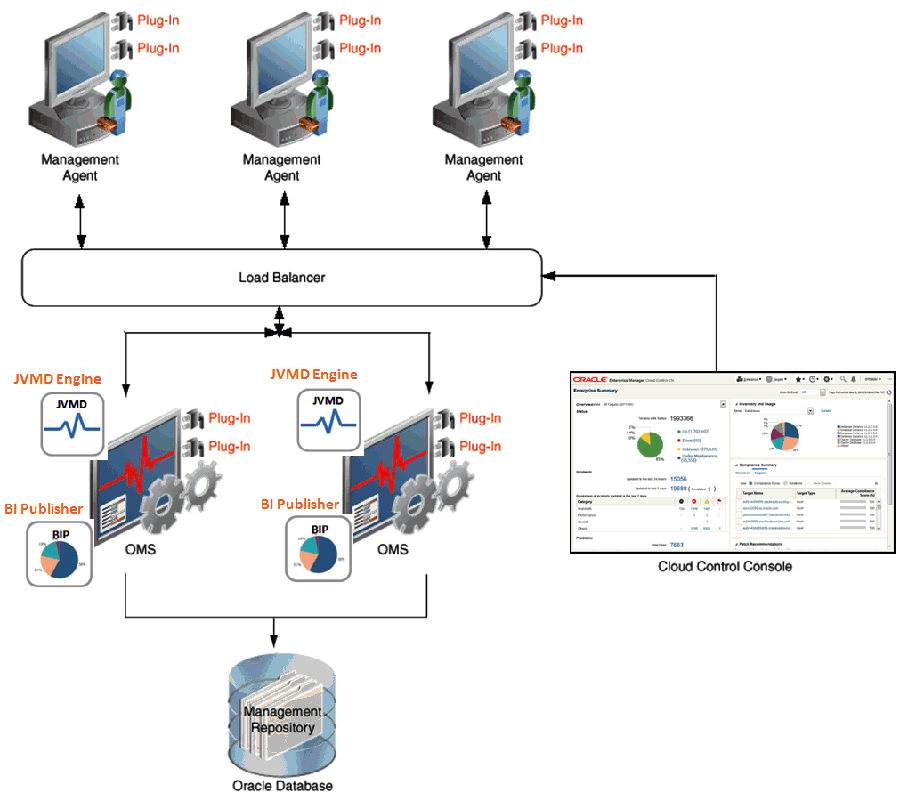
Architecture of Enterprise Manager Cloud Control
Enterprise Manager Cloud Control includes the following components:
- Oracle Management Agent
- Oracle Management Service
- Oracle Management Repository
- Plug-ins
The Oracle Management Agent (OMA) is a pivotal component in the architecture of Oracle's Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, serving as the essential liaison between the managed targets and the Oracle Management Service (OMS). Operating as a background process, OMA is generally deployed on each monitored host and is responsible for performing tasks that range from data collection to executing administrative operations.
OMA Core Functions:
- Data Collection: The agent is responsible for gathering performance metrics, configuration data, and compliance details from the managed targets. This data is relayed to the Oracle Management Repository via the Oracle Management Service.
- Job Execution: Oracle Management Agent facilitates the execution of administrative tasks such as patching, backup, or application deployments. Commands from the OMS are relayed to the OMA, which then executes them on the managed target.
- Event Monitoring: OMA keeps a vigilant eye on the event conditions defined in the monitoring templates and immediately notifies the OMS if an event condition is triggered.
- Configuration Management: The agent is responsible for tracking configuration changes in the managed targets and reporting this information back to the OMS for inventory management, configuration comparisons, and compliance assessments.
- Provisioning and Patching: Oracle Management Agent automates the deployment of software and patches to managed targets, thus streamlining administrative tasks and ensuring consistency and compliance across the IT environment.
Architectural Significance:
- Decentralization: By offloading monitoring and management tasks from the central OMS to local agents, Enterprise Manager achieves a scalable, decentralized architecture.
- Reduced Latency: Since the agent resides on or near the managed target, it reduces network latency, enabling quicker data collection and task execution.
- Fault Tolerance: The agent queues up data and operations in case of network failures or if the OMS is unreachable. Once the connection is restored, it synchronizes with the OMS, ensuring data integrity and operational continuity.
- Security: All communication between the OMA and the OMS is encrypted and authenticated, thereby enhancing the overall security of the management framework.
- Resource Optimization: OMA is designed to minimize its footprint on the host system, thus ensuring that its operations do not significantly impact the performance of the managed targets.
- Target Agnostic: Oracle Management Agents are versatile and can handle a broad array of target types, including databases, application servers, and even non-Oracle hardware and software, when appropriately configured.
In summary, the Oracle Management Agent is a critical element in Oracle's Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, fulfilling a multi-faceted role that extends from monitoring and data collection to configuration management and operational task execution. Its role is foundational to achieving a scalable, secure, and efficient management infrastructure.
OEM Legacy Diagram
Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) has built-in management capabilities that enable DBAs and Apps DBAs to monitor and manage the complete Oracle IT infrastructure including the Databases and Applications on Cloud as well as On-Premise from a single console.
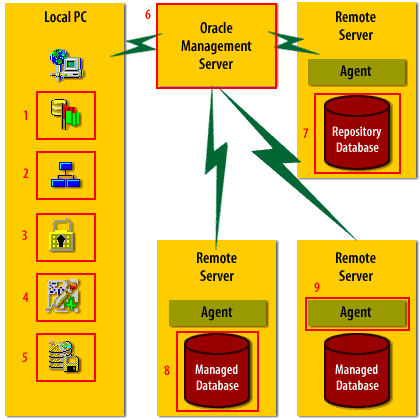
- Instance Manager: Used to startup and shutdown an Oracle database. Used to startup and shutdown an Oracle database.
- Schema Manager: Used to create and manage tables, indexes, views, and other schema objects.
- Security Manager: Used to grant system and object privileges to users, and to otherwise manage database security.
- SQLPlus Worksheet: Used to execute ad-hoc SQL statements, and SQL scripts.
- Storage Manager: Used to manage tablespaces and datafiles.
- Oracle Management Server: The Management Server represents the middle-tier, and is where event monitoring logic and job submission logic are implemented. The Management Server also runs the web browser interface.
- Repository Database: This is the database where OEM stores its information. It does not necessarily need to be physically on the same machine as the Oracle Management Server software.
- Managed Database: Any number of remote databases may be managed using Enterprise Manager.
- Oracle's Intelligent Agent has been deprecated since the release of Oracle 10g.
Oracle Management Agent (Management Agent) The Management Agent is an integral software component that enables you to convert an unmanaged host to a managed host in the Enterprise Manager system. The Management Agent works in conjunction with the plug-ins to monitor the targets running on that managed host.
Software runs on each database server, and is responsible for ensuring that scheduled jobs for that server are actually run. When you schedule a job from the console, the management server stores that information in the repository, and communicates it to the appropriate agent. The agent ensures that the job gets run, and reports status back to the management server. That way, network outages do not prevent scheduled jobs from running.