| Lesson 2 | Overview of the Oracle architecture |
| Objective | Describe the layout of the Oracle components. |
Overview of Oracle architecture
Question: What is the goal of Oracle tuning?
The goal of Oracle tuning is to optimize all Oracle tasks such that all transactions complete in the minimum amount of time and improve efficiency of Oracle database systems. This involves identifying and addressing any factors that may be causing the database to operate slowly or inefficiently, such as poorly designed database schema, inefficient SQL queries, or inadequate hardware resources. Oracle tuning involves various techniques and strategies, including configuring database parameters, optimizing SQL queries, tuning database schema, and optimizing hardware resources. The ultimate goal of Oracle tuning is to ensure that the database operates at maximum efficiency and performance, which can lead to improved productivity, reduced downtime, and better overall user experience.
The goal of Oracle tuning is to optimize all Oracle tasks such that all transactions complete in the minimum amount of time and improve efficiency of Oracle database systems. This involves identifying and addressing any factors that may be causing the database to operate slowly or inefficiently, such as poorly designed database schema, inefficient SQL queries, or inadequate hardware resources. Oracle tuning involves various techniques and strategies, including configuring database parameters, optimizing SQL queries, tuning database schema, and optimizing hardware resources. The ultimate goal of Oracle tuning is to ensure that the database operates at maximum efficiency and performance, which can lead to improved productivity, reduced downtime, and better overall user experience.
Review of the Oracle architecture
An Oracle instance is a memory region, files on disk, and a set of server processes. Each of these components can be tuned independently. To understand this point, let's briefly review the Oracle architecture with an eye towards tuning.
The MouseOver below shows the opportunities for Oracle tuning within each of these areas.
The MouseOver below shows the opportunities for Oracle tuning within each of these areas.
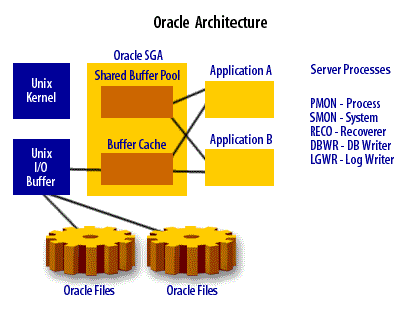
| 1. Memory region | The efficient allocation of the Oracle system global areas (SGA) can have a huge impact upon database performance. The larger the SGA, the more data and programs Oracle will be able to reside in RAM memory. The more memory in the SGA, the faster your database will perform. |
| 2. Disk data files | The Oracle data files on disk constitute one of the largest components of response time. The more disk I/O, the slower the transaction. One of the goals of Oracle tuning is to minimize I/O and ensure that all disk files are evenly spread across the disks. |
| 3. Oracle processes | The Oracle processes that make up the Oracle instance have an impact upon database performance. For example, when parallel query is used, Oracle will create additional server processes to speed the query. |
| 4. External application connections | The external connections to Oracle and the SQL that they issue will also have a huge impact upon performance. Identifying inefficient SQL can help you tune your application. |
Components that make up Oracle Architecture
Oracle database architecture consists of several components that work together to provide a comprehensive database management system. These components include:
- Oracle Instance: The Oracle instance is a set of processes and memory structures that access an Oracle database. It includes the background processes and the memory structures that handle the requests of users and applications.
- Oracle Database: The Oracle database is the collection of data that is managed by the Oracle instance. It consists of a set of physical files on disk, including data files, redo log files, and control files.
- Oracle Processes: Oracle processes are the operating system processes that perform tasks for the Oracle instance. These processes include background processes, such as the database writer (DBWR) and log writer (LGWR), as well as user processes, which handle requests from clients.
- Oracle Memory Structures: Oracle uses various memory structures to store and manage data, including the system global area (SGA) and the program global area (PGA). The SGA is a shared memory region that stores data and control information for the Oracle instance, while the PGA is a memory region used by individual Oracle processes.
- Oracle Data Files: Oracle data files are physical files on disk that store the actual data in the database. These files contain the data for tables, indexes, and other database objects.
- Oracle Redo Log Files: Oracle redo log files are physical files on disk that store information about changes made to the database. This information is used to recover the database in the event of a failure or outage.
- Oracle Control Files: Oracle control files are physical files on disk that store metadata about the database, such as the names and locations of data files and redo log files.