| Lesson 10 | Splitting and merging partitions |
| Objective | Split and merge partitions. |
Splitting and Merging Partitions in Oracle 19c
In Oracle 19c, partitioning is a powerful feature that allows tables and indexes to be divided into smaller, more manageable pieces while still appearing as a single object to users. The processes for 1) splitting one partition into two partitions and 2) merging two partitions into one involve specific operations that modify the partitioning structure of a table or index.
1. Splitting One Partition into Two
Overview:
Steps:
2. Merging Two Partitions into One
Overview:
Steps:
Key Considerations:
These operations allow flexibility in managing partitioned tables and indexes, enabling efficient organization and querying of data in Oracle 19c.
1. Splitting One Partition into Two
Overview:
- Splitting a partition involves dividing an existing partition into two, based on a specific boundary value.
Steps:
-
Use the
ALTER TABLECommand:- Specify the partition to be split and the new boundary values for the two resulting partitions.
- Optionally, you can define different tablespaces for the resulting partitions.
-
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name SPLIT PARTITION partition_name AT (boundary_value) INTO ( PARTITION new_partition_1 TABLESPACE tablespace_1, PARTITION new_partition_2 TABLESPACE tablespace_2 ); -
Example:
Suppose you have a table
salespartitioned by range on thesales_datecolumn, and you want to split thep1partition into two partitions at the date01-JAN-2023:ALTER TABLE sales SPLIT PARTITION p1 AT (TO_DATE('01-JAN-2023', 'DD-MON-YYYY')) INTO ( PARTITION p1_1 TABLESPACE ts1, PARTITION p1_2 TABLESPACE ts2 ); -
Result:
- The original
p1partition is divided intop1_1andp1_2. - Data is redistributed based on the specified boundary value.
- The original
2. Merging Two Partitions into One
Overview:
- Merging partitions combines two adjacent partitions into one, removing the boundary between them.
Steps:
-
Use the
ALTER TABLECommand:- Specify the two partitions to merge.
-
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE table_name MERGE PARTITIONS partition_1, partition_2 INTO PARTITION new_partition_name TABLESPACE tablespace_name; -
Example:
Suppose you have a table
salespartitioned by range, and you want to merge thep1andp2partitions into a new partition calledp_merged:ALTER TABLE sales MERGE PARTITIONS p1, p2 INTO PARTITION p_merged TABLESPACE ts_merged; -
Result:
- The
p1andp2partitions are combined intop_merged. - Data from both partitions is consolidated into a single partition.
- The
Key Considerations:
-
Data Redistribution:
- In both operations, Oracle redistributes or consolidates data as necessary. Ensure there is sufficient space in the target tablespace(s).
-
Partition Boundaries:
- For splitting, define the boundary value correctly to ensure proper data distribution.
- For merging, the partitions must be adjacent, i.e., share a common boundary.
-
Index Management:
- If the table has local indexes, they are automatically managed during partition operations.
- Global indexes may require maintenance or rebuilding after the operation.
-
Performance Implications:
- Both operations can be resource-intensive, especially for large partitions. Consider performing them during maintenance windows.
-
Backup and Testing:
- Always back up the table before making structural changes.
- Test the operations in a non-production environment to ensure correctness.
These operations allow flexibility in managing partitioned tables and indexes, enabling efficient organization and querying of data in Oracle 19c.
Expert Oracle Indexing and Access Paths
You create partitioned tables in order to increase performance and availability and reduce maintenance time.
However, changing conditions or an incorrect initial design may require you to alter the way the partitions are divided.
If this occurs, one option is to either split one partition into two, or merge two partitions into one.
You can split a partition into two separate partitions with the command:
This command will also split the associated local index partition. All affected index partitions, both local and global, will be marked as unusable and will have to be rebuilt.
You can split a partition into two separate partitions with the command:
ALTER TABLE table_name SPLIT PARTITION partition_name
AT ( '40-001' )
INTO ( PARTITION new_partition_name1
PARTITION new_partition_name2)
This command will also split the associated local index partition. All affected index partitions, both local and global, will be marked as unusable and will have to be rebuilt.
-
Merging Partitions
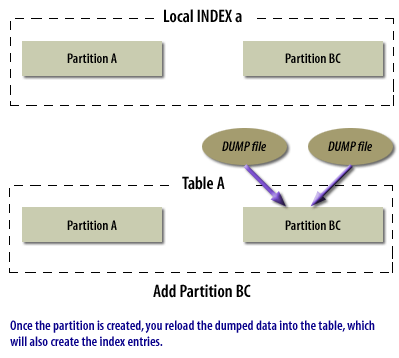
Merging partitions is not as simple as the other partitioning modifications discussed so far. There is not a single command that will merge partitions. Instead, you must go through a four-step process:
- Dump the data from the two partitions to be merged into a dump file
- Drop the partitions you want to merge from the table
- Add the new partitions you want to create to the table
- Reload the data from the dump file
As with the modifications above, any local indexes will be automatically dropped and recreated, and any affected global index partitions or any nonpartitioned indexes will be marked as unusable.
The following series of images illustrate the process of merging partitions:
Merging Partitions in Oracle
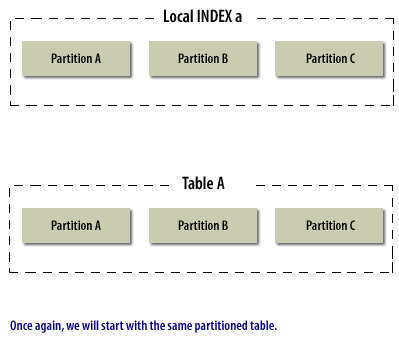
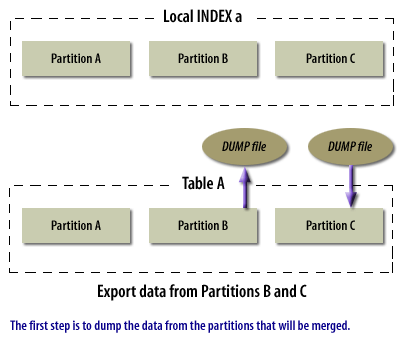
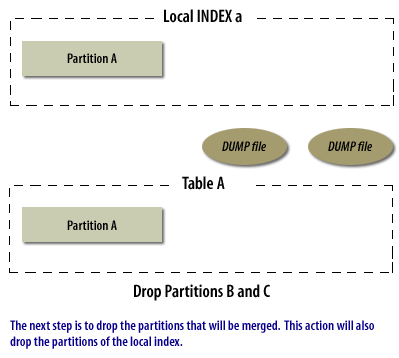
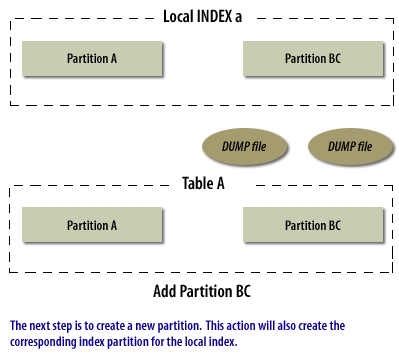
Merging Oracle Partitions
Use the
statement to merge the contents of two partitions into one partition. The two original partitions are dropped, as are any corresponding local indexes. You cannot use this statement for a hash-partitioned table or for hash subpartitions of a composite *-hash partitioned table. You cannot merge partitions for a reference-partitioned table. Instead, a merge operation on a parent table will cascade to all descendant tables. However, you can use the DEPENDENT TABLES clause to set specific properties for dependent tables when you issue the merge operation on the master table to merge partitions or subpartitions
The next lesson is the module conclusion.
ALTER TABLE ... MERGE PARTITION
statement to merge the contents of two partitions into one partition. The two original partitions are dropped, as are any corresponding local indexes. You cannot use this statement for a hash-partitioned table or for hash subpartitions of a composite *-hash partitioned table. You cannot merge partitions for a reference-partitioned table. Instead, a merge operation on a parent table will cascade to all descendant tables. However, you can use the DEPENDENT TABLES clause to set specific properties for dependent tables when you issue the merge operation on the master table to merge partitions or subpartitions
The next lesson is the module conclusion.