| Lesson 4 | Writing queries that use DEREF |
| Objective | Write a query using a DEREF data type to retrieve related data. |
Writing Queries that use DEREF in Oracle
In this lesson, we will look at an example that uses a
DEREF data type to retrieve related data.
DEREF is a dereference operator that returns the value of an object. Unlike the VALUE operator, it takes a correlation argument[1], which is a REF (reference) to the object. Therefore, if you have a REF column within a table and you want to retrieve the target object instead of the reference to it, use DEREF. The following series of images shows the syntax for using the DEREF data type:

- DEREF is an operator, which dereferences a reference.
- DEREF returns the reference object.
- DEREF accepts a correlation argument, which is the reference "REF" to an object
SELECT DEREF(object_reference) FROM object_table_name WHERE column_name="variable_value";
When the REF argument is passed to the DEREF operator, it returns the object.
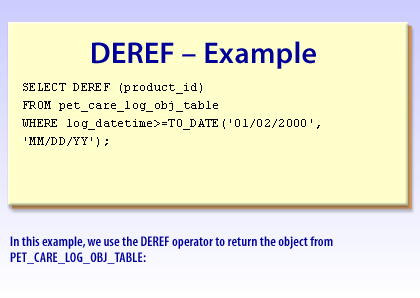
SELECT DEREF (product_id) FROM pet_care_log_obj_table
WHERE log_datetime>=TO_DATE('01/02/2000', 'MM/DD/YY');
DEREF syntax
DEREF returns the object instance that the REF value points to. This is more easily explained with a simple example.
In this case, DEREF is passed the REF value for the correlation ID of the inventory_tbl:
The object instance associated with the REF value of item_id 1 is returned:
SELECT DEREF(REF(i)) FROM inventory_tbl i WHERE item_id = 1;
The object instance associated with the REF value of item_id 1 is returned:
DEREF(REF(I))(ITEM_ID, NUM_IN_STOCK, REORDER_STATUS, PRICE(DISCOUNT_RA ---------------------------------------------------------------------- INVENTORY_OBJ(1, 10, 'IN STOCK', DISCOUNT_PRICE_OBJ(.1, 75))
Build Oracle DEREF Query
To build a "DEREF query in Oracle", you must be working with object-relational features, specifically with **REFs** (references to objects). The `DEREF` operator is used to **dereference** a REF column to access the **object's attributes**.
✅ Overview: What Is `DEREF`?
🧱 Prerequisites (Steps to Set Up a `DEREF` Query):
🛠️ Notes:
🔍 Optional: Filter by Attribute in the REFERENCED Object
❗ Common Errors to Avoid
✅ Summary of Required Steps
✅ Overview: What Is `DEREF`?
DEREF(ref_column)lets you access the **full object** pointed to by a **REF**.- You can then retrieve **attributes of the object** in the SELECT clause.
🧱 Prerequisites (Steps to Set Up a `DEREF` Query):
- Create an Object Type
CREATE TYPE department_t AS OBJECT ( deptno NUMBER, dname VARCHAR2(100) );
- Create an Object Table Based on the Type
CREATE TABLE department_tab OF department_t;
- Create Another Table That Stores REFs
CREATE TABLE emp_ref_tab ( empname VARCHAR2(100), dept_ref REF department_t SCOPE IS department_tab );
- Insert Data into the Object Table
INSERT INTO department_tab VALUES (10, 'ACCOUNTING'); INSERT INTO department_tab VALUES (20, 'RESEARCH');
- Insert REFs into the Ref Table
DECLARE d_ref REF department_t; BEGIN SELECT REF(d) INTO d_ref FROM department_tab d WHERE deptno = 10; INSERT INTO emp_ref_tab VALUES ('SMITH', d_ref); END; / - Write a `DEREF` Query to Access Object Attributes
SELECT e.empname, DEREF(e.dept_ref).dname AS department_name FROM emp_ref_tab e;
🛠️ Notes:
🔍 Optional: Filter by Attribute in the REFERENCED Object
SELECT empname FROM emp_ref_tab WHERE DEREF(dept_ref).deptno = 10;
❗ Common Errors to Avoid
| Error | Reason |
|---|---|
ORA-00904: invalid identifier |
Using DEREF on a non-REF column |
ORA-22922: nonexistent REF |
The REF points to a deleted row (i.e., a dangling reference) |
IS DANGLING missing |
Always test with IS DANGLING if deletion may have occurred |
✅ Summary of Required Steps
- Create an object type (
CREATE TYPE) - Create an object table from that type
- Create a REF table with a
REFcolumn - Use
REF(...)to insert a reference into the REF table - Use
DEREF(ref_column)to access the object's attributes
Build Oracle DEREF Query in Oracles
Build a query by using DEREF and then complete the required entry fields to connect to the database.
- Then begin to build the SQL.
- Select the DEREF of the reference from the appropriate table, and execute the SQL.
- After the process is completed, SQL*Plus displays the result of the compilation of your query, click exit.
- Object-Relational Queries
Object-Relational queries are queries which can handle data object features on the existing relational data environment. REF is one of most important data structures in Object-Relational Databases and can be explained as a logical pointer to define the link between two tables with a similar function. There are three ways of writing REF join queries which are:
- REF Join,
- Path Expression Join and
- DEREF/VALUE Join.
PL/SQL Programming
Using DEREF in a SELECT INTO Statement
DECLARE emp employee_typ; emp_ref REF employee_typ; emp_name VARCHAR2(50); BEGIN SELECT REF(e) INTO emp_ref FROM employee_tab e WHERE e.employee_id = 370;
The following assignment raises an error, not allowed in PL/SQL
emp_name := emp_ref.first_name || ' ' || emp_ref.last_name;
emp := DEREF(emp_ref);
//is not allowed, cannot use DEREF in procedural statements
SELECT DEREF(emp_ref) INTO emp FROM DUAL; -- use dummy table DUAL emp_name := emp.first_name || ' ' || emp.last_name; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(emp_name); END; /
In the next lesson, we will explain when PL/SQL is appropriate or required for querying object tables.
Now that you have learned about the
DEREF data type, click the link below to learn more about retrieving related data.
[1]Correlation argument: A correlation argument is a parameter, which is passed when a function is used, e.g. the VALUE finction requires the table alias to be passed as a parameter or correlation argument.