| Lesson 6 | Open database backups |
| Objective | List the requirements for an open database backup. |
Requirements for Open Database Backup in Oracle
If a business requires its database to run 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, there are important implications for backup and recovery. If the database cannot be shut down to perform backups, open database backup must be selected as the most prudent backup and recovery strategy. An open database backup allows the DBA to perform backups of all the tablespaces or individual datafiles while the database is in use.
Advantages and Disadvantages for open Database Backup
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
|---|---|
| Maintain high database availability: When using an open database backup, the database is available for process access during the backup and the business transactions will not be interrupted because of the backup. |
More training required for the DBA: Because an open database backup is a complicated process (compared to the closed database backup), a DBA will need more training to handle the process. |
| Can be done at a tablespace or datafile level: A DBA may choose to backup all the datafiles for a specific tablespace or just individual datafiles for a tablespace. | More error-prone: An online database backup is more error-prone because of additional operator interaction. Thus, it is best to use tested scripts to automate the process. |
| Allows recovery to point-in-time: With an open database backup, the DBA may choose to recover the database to a certain point of time. |
Overview of Database Backup and Recovery
The focus in Oracle Database backup and recovery is on the physical backup of database files, which permits you to reconstruct your database. Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN), a command-line tool, is the method preferred by Oracle for efficiently backing up and recovering your Oracle database. The files protected by the backup and recovery facilities built into RMAN include
- data files,
- control files,
- server parameter files, and
- archived redo log files.
Requirements for Backups of Tablespaces
Before a DBA can perform backups of tablespaces or a specific datafile while the database is online, two criteria must be met:
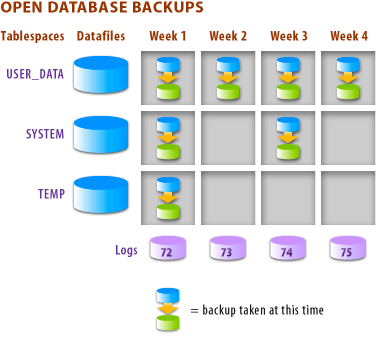
The image below shows the routine a DBA must follow to make an open database backup. The DBA backs up
All the backup actions are recorded respectively in the redo logs.
- The database must be operating in ARCHIVELOG mode; and
- The ARCH process must be enabled. This can be done automatically at instance startup or manually following instance startup.
- Datafiles
- Control files
- Parameter files
- Password files
- Archived redo log files
The image below shows the routine a DBA must follow to make an open database backup. The DBA backs up
- the tablespace USER_DATA once a week,
- the tablespace SYSTEM once a month, and
- the tablespace TEMP once every two weeks.
All the backup actions are recorded respectively in the redo logs.
Information about the required files is found in data dictionary views. You can use V$DATAFILE, V$CONTROLFILE, and DBA_DATA_FILES just like you did for closed database backups. Because an open database backup is performed by backing up tablespaces or individual files, make sure you query DBA_DATA_FILES to find the required datafiles and their respective tablespaces. To obtain information about archived redo log files, query data dictionary views
- V$ARCHIVED_LOG,
- V$ARCHIVE_DEST,
- V$LOG_HISTORY, and
- V$DATABASE.
ARCHIVE LOG LIST in the Server Manager.
This command gives the DBA information on the current log mode and status of archiving for the database.The next lesson explains open database backup options.