| Lesson 7 | Monitoring Recovery Status via Data Dictionary Views |
| Objective | Obtain Recovery Status Information using the Data Dictionary Views |
Monitoring Recovery Status via Data Dictionary Views
Can I obtain Recovery Status Information of a database using the Data Dictionary Views in Oracle 19c?
You can obtain Recovery Status Information of a database using Data Dictionary Views in Oracle 19c. Some of the key Data Dictionary Views that provide information on the recovery status include:
Additional Notes:
-
V$RECOVERY_FILE_DEST
- Provides information about the Fast Recovery Area (FRA) usage, space allocation, and recovery-related files.
-
SELECT * FROM V$RECOVERY_FILE_DEST;
-
V$RECOVERY_STATUS
- Shows the current recovery session status.
-
SELECT * FROM V$RECOVERY_STATUS; - Note: This view may be empty if there is no active recovery session.
-
V$RECOVERY_PROGRESS
- Provides details on recovery progress when performing media recovery or instance recovery.
-
SELECT * FROM V$RECOVERY_PROGRESS;
-
V$RECOVERY_LOG
- Displays information about archived redo logs that are required for recovery.
-
SELECT * FROM V$RECOVERY_LOG;
-
V$ARCHIVED_LOG
- Shows all archived redo logs, including logs that might be required for recovery.
-
SELECT SEQUENCE#, APPLIED, STATUS FROM V$ARCHIVED_LOG ORDER BY SEQUENCE#;
-
V$LOG_HISTORY
- Provides a history of redo logs that were written and archived.
-
SELECT * FROM V$LOG_HISTORY;
-
V$BACKUP
- Indicates whether a tablespace or datafile is in backup mode, useful for hot backups.
-
SELECT * FROM V$BACKUP WHERE STATUS != 'NOT ACTIVE';
-
V$DATAFILE_HEADER
- Displays information about datafile headers, including fuzzy status (indicating if recovery is needed).
-
SELECT FILE#, STATUS, FUZZY FROM V$DATAFILE_HEADER;
-
V$INSTANCE_RECOVERY
- Shows the status of instance recovery, including log target, log read/write speeds, etc.
-
SELECT * FROM V$INSTANCE_RECOVERY;
-
V$FAST_START_TRANSACTIONS
- Displays transactions that need fast-start rollback after an instance crash.
-
SELECT * FROM V$FAST_START_TRANSACTIONS;
Additional Notes:
-
If Data Guard is enabled, you may also use:
SELECT * FROM V$DATAGUARD_STATUS;to check Data Guard recovery messages. - For RMAN Recovery Catalog, you can query RC_BACKUP, RC_ARCHIVED_LOG, and RC_DATABASE views.
There are two data dictionary views that provide information about recovery status:
V$RECOVERY_STATUS and V$RECOVERY_FILE_STATUS. You can query the two views as soon as the
ALTER DATABASE RECOVERYcommand is issued. The
V$RECOVERY_STATUS view shows you all files that require recovery.
The V$RECOVERY_FILE_STATUS view gives you the recovery status of each file. During recovery, the information for these views exists only in the PGA(Program Global Area)[1] of the server process. The PGA is a temporary area of memory used by the server process that is connected to the user. This area disappears when the connection ends. The above views are therefore only available to the user who issued the recovery command. In addition, the views become inaccessible after the recovery process is terminated.
The following series of images demonstrates how to obtain "recovery status information" during a recovery using these two data dictionary views.
Monitoring 'Recovery Status' via the 'Data Dictionary Views'
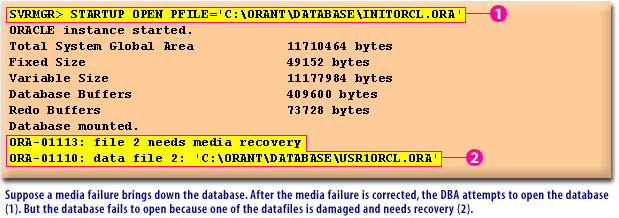
The DBA attempted to start the database using the following command:
SQL> STARTUP OPEN PFILE='C:\ORANT\DATABASE\INITORCL.ORA'
However, the database did not fully open because one of the datafiles required media recovery. The error messages displayed indicate:
ORA-01113: file 2 needs media recovery ORA-01110: data file 2: 'C:\ORANT\DATABASE\USR1ORCL.ORA'
This means that file 2 (`USR1ORCL.ORA`) is in an inconsistent state and needs media recovery before the database can be opened. How to Fix This Issue:
-
Check the status of the affected file:
SELECT FILE#, STATUS, ERROR FROM V$RECOVER_FILE; -
If the database is in ARCHIVELOG mode, perform recovery:
RECOVER DATAFILE 'C:\ORANT\DATABASE\USR1ORCL.ORA'; -
Apply archive logs if prompted.
- (No code provided for this step)
-
Once recovery is complete, open the database:
ALTER DATABASE OPEN;
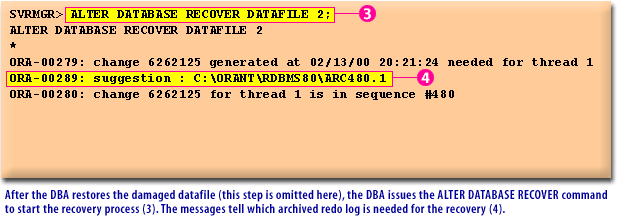
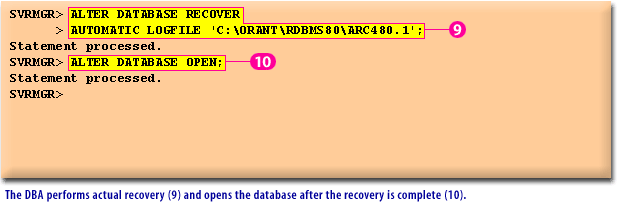
ALTER DATABASE RECOVER command to start the recovery process (3). The messages tell which archived redo log is needed for the recovery (4).
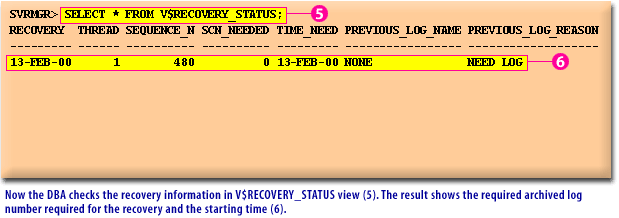
V$RECOVERY_STATUS view (5).
The result shows the required archived log number required for the recovery and the starting time (6).
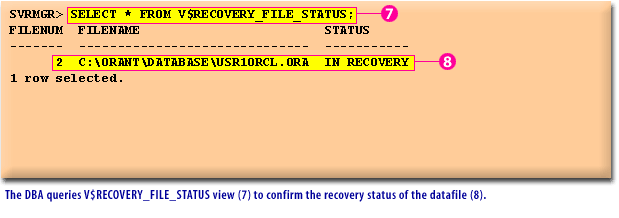
V$RECOVERY_FILE_STATUS view (7) to confirm the recovery status of the datafile (8).
SQL> STARTUP OPEN PFILE='C:\ORANT\DATABASE\INITORCL.ORA'
ORACLE instance started.
Total System Global Area 11710464 bytes
Fixed Size 49152 bytes
Variable Size 11177984 bytes
Database Buffers 409600 bytes
Redo Buffers 73728 bytes
Database mounted.
ORA-01113: file 2 needs media recovery
ORA-01110: data file 2: 'C:\ORANT\DATABASE\USR1ORCL.ORA'
SQL> ALTER DATABASE RECOVER DATAFILE 2;
ALTER DATABASE RECOVER DATAFILE 2
*
ORA-00279: change 6262125 generated at 02/13/00 20:21:24 needed for thread 1
ORA-00289: suggestion : C:\ORANT\RDBMS80\ARC480.1
ORA-00280: change 6262125 for thread 1 is in sequence #480
SQL> SELECT * FROM V$RECOVERY_STATUS;
RECOVERY THREAD SEQUENCE_N SCN_NEEDED TIME_NEED REVIOUS_LOG_NAME PREVIOUS_LOG_ REASON
-------- ------ ---------- ---------- ------------------
----------------- ------------------------------------
13-FEB-00 1 480 0 13-FEB-00 NONE
NONE NEED LOG
1 row selected.
SQL> SELECT * FROM V$RECOVERY_FILE_STATUS;
FILENUM FILENAME STATUS
------- ------------------------------------ --------------
2 C:\ORANT\DATABASE\USR1ORCL.ORA IN RECOVERY
1 row selected.
SQL> ALTER DATABASE RECOVER
> AUTOMATIC LOGFILE 'C:\ORANT\RDBMS80\ARC480.1';
Statement processed.
SQL> ALTER DATABASE OPEN;
Statement processed.
SQL>
To see the command lines and their results for the whole process, click the View SlideShow link. The next lesson concludes this module.
[1]PGA: The Program/Process Global Area (PGA) is a memory region that contains data and controls information for a single server process or a single background process. The information contained in the PGA could be sort data, session information, cursor state, or stack space. The PGA is allocated when a process is created and de-allocated when the process is terminated.