| Lesson 3 | SQL WHERE clause |
| Objective | Use WHERE to select specific rows of a table. |
SQL WHERE Clause
Often times you will want queries to return only a subset of the entire database. For example, when searching for a list of books by a specific author. The SELECT statement's WHERE clause allows you to select only data from rows that satisfy a certain condition.
A clause further defines a statement. For example the following statement returns all rows:
Adding the WHERE clause such as WHERE Author='Hemingway', further defines the statement to return only rows in which the author equals Hemingway. The following SQL query returns books by Hemingway.
The WHERE clause uses comparison and logical operators to select rows meeting the specified condition. The following SlideShow describes how the WHERE clause is used:
SELECT * FROM BookTable
Adding the WHERE clause such as WHERE Author='Hemingway', further defines the statement to return only rows in which the author equals Hemingway. The following SQL query returns books by Hemingway.
SELECT * FROM BookTable WHERE Author = 'Hemingway'
The WHERE clause uses comparison and logical operators to select rows meeting the specified condition. The following SlideShow describes how the WHERE clause is used:
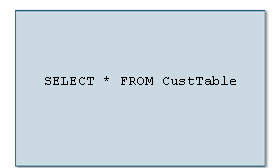
SELECT * FROM CustTableThis part of the SELECT statement says to select all columns from the CustTable table.



SELECT * FROM CustTable WHERE ST='AZ'The complete statement. This statement will return all columns from rows where state equals Arizona.
Using the WHERE clause
The following example uses the WHERE clause to get the total number of units in stock for all discontinued products in the Products table.
SELECT SUM([Units In Stock]) AS [Units Remaining] FROM Products WHERE (Discontinued = 'True')
SQL has several operators that allow the SELECT statement to be very selective about the data returned from a query.
The following tables list the comparison and logical operators used with SQL:
The following statement uses the logical operator AND to select rows where state equals Arizona and last name equals Henry:
In the next lesson, the ORDER BY clause to sort rows in a table will be discussed.
- Comparison Operators:
Comparison Operators Symbol 1Function = Equal <> Not equal > Greater than >= Greater than or equal < Less than <= Less than or equal - Logical Operators
Logical Operators Operator Function AND Returns TRUE if all conditions are true OR Returns TRUE if one or more conditions are true NOT Returns TRUE if the condition is false
The following statement uses the logical operator AND to select rows where state equals Arizona and last name equals Henry:
SELECT * FROM CustTable WHERE ST = 'AZ' AND LName = 'Henry'
In the next lesson, the ORDER BY clause to sort rows in a table will be discussed.