| Lesson 4 | SQL Server services |
| Objective | Describe the Services available in Microsoft SQL Server |
Services available in Microsoft SQL Server
Microsoft SQL Server uses services to provide the underlying functionality that enables you to access SQL Server.
A service is a process or function that runs autonomously in the background under Windows 10 or Windows Server 2016.
A service must start with a user name and password (known as a security context) to function.
The user name and password that you specify must correspond to a person who has access to the resources used by the service.
The following four services are available in Microsoft SQL Server :
Each of these four services can be in one of three states:
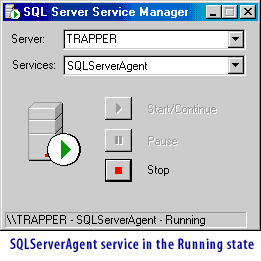
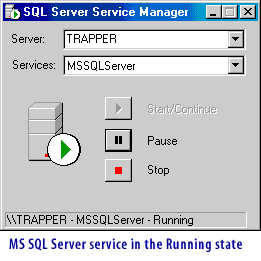
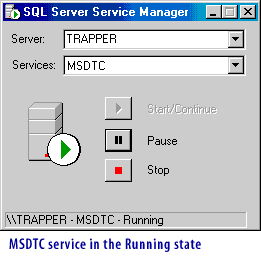
The following series of images illustrates the four services in the Running state under Windows.
- MSDTC:Used to manage distributed transactions.
(You will learn more about distributed transactions in the third course in this series.) - MSSQLServer: Enables SQL Server to function. If the MSSQLServer service is not running, SQL Server will not respond to queries and requests.
- SQLServerAgent:Handles all scheduling within SQL Server . (You will learn more about scheduling later in this course.)
- Microsoft Search:Search engine service for use with full-text searches. This service is only available if you have chosen to install the full-text search when you initially installed SQL Server .
Each of these four services can be in one of three states:
- Running:Fully operational and able to provide the functionality designed for the service.
- Paused:Allows existing users to complete tasks, but does not allow any new connections.
- Stopped:Does not perform any of the functionality designed for the service.
The following series of images illustrates the four services in the Running state under Windows.
Microsoft SQL Server Express 2022
Microsoft still offers SQL Server Express as part of "SQL Server 2022". SQL Server Express is a free, lightweight edition of SQL Server, designed for learning, development, and small-scale applications.
Key Features of SQL Server 2022 Express
Limitations of SQL Server Express
How to Download SQL Server 2022 Express
Should You Use SQL Server Express?
Consider SQL Server Standard or Enterprise if:
Conclusion: SQL Server Express 2022 is still available, remains free, and is useful for development and small applications. However, it has size and performance limitations, making it unsuitable for large-scale enterprise solutions.
Key Features of SQL Server 2022 Express
- Free to use: No licensing costs.
- Lightweight and easy to install.
- Supports up to 10 GB per database.
- Can use up to 4 cores and 1 GB of RAM.
- Includes SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) for database management.
- Supports local and remote connections.
Limitations of SQL Server Express
- Database size limit: 10 GB per database.
- Memory limit: 1 GB RAM per instance.
- CPU limit: Uses up to 4 logical processors.
- No SQL Agent: Lacks built-in job scheduling.
- Limited high availability features (No Always On, Mirroring).
How to Download SQL Server 2022 Express
- Go to the official Microsoft SQL Server Express Download Page.
- Select SQL Server Express 2022.
- Download the installer and follow the setup wizard.
Should You Use SQL Server Express?
- You're developing small applications.
- You need a free, local database for testing.
- You're a student or learning SQL Server.
Consider SQL Server Standard or Enterprise if:
- You need more than 10 GB per database.
- You require high availability features.
- You need SQL Agent for job scheduling.
Conclusion: SQL Server Express 2022 is still available, remains free, and is useful for development and small applications. However, it has size and performance limitations, making it unsuitable for large-scale enterprise solutions.
How to Start and Stop the SQL Server Browser Service for SQL Server Express 2022
The SQL Server Browser Service is responsible for handling incoming requests for SQL Server Express instances when connecting using named instances or dynamic ports. By default, it is disabled in SQL Server Express.
Method 1: Using SQL Server Configuration Manager
Start the SQL Server Browser Service
Stop the SQL Server Browser Service
Method 2: Using Windows Services (services.msc)
Method 3: Using Command Prompt (CMD)
Method 4: Using PowerShell
Troubleshooting Issues
Conclusion You can start/stop the SQL Server Browser in SQL Server Express 2022 using:
Method 1: Using SQL Server Configuration Manager
Start the SQL Server Browser Service
- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager:
- Press
Win + R, typecompmgmt.msc, and press Enter. - Expand Services and Applications → Click SQL Server Configuration Manager.
- If it’s missing, find SQLServerManager16.msc (for SQL Server 2022).
- Press
- Navigate to SQL Server Services:
- Expand SQL Server Configuration Manager → Click SQL Server Services.
- Find "SQL Server Browser":
- Right-click SQL Server Browser → Select Properties.
- Change the Start Mode:
- Go to the Service tab.
- Set Start Mode to Automatic (Optional if you want it to always start with Windows).
- Start the Service:
- Right-click SQL Server Browser → Click Start.
Stop the SQL Server Browser Service
- Right-click SQL Server Browser in SQL Server Configuration Manager.
- Click Stop.
Method 2: Using Windows Services (services.msc)
- Press
Win + R, typeservices.msc, and press Enter. - Scroll down and find SQL Server Browser.
- Right-click it and choose Start or Stop.
- If needed, set Startup Type to Automatic in Properties.
Method 3: Using Command Prompt (CMD)
-
Start SQL Server Browser
net start "SQL Server Browser"
-
Stop SQL Server Browser
net stop "SQL Server Browser"
Method 4: Using PowerShell
-
Start SQL Server Browser
Start-Service -Name "SQLBrowser"
-
Stop SQL Server Browser
Stop-Service -Name "SQLBrowser"
Troubleshooting Issues
- Service Won't Start?
- Open SQL Server Configuration Manager → Go to Protocols for SQLEXPRESS.
- Ensure TCP/IP and Named Pipes are enabled.
- Restart the SQL Server Service.
- SQL Server Browser Service Missing?
- Reinstall SQL Server Express and select SQL Server Browser during installation.
Conclusion You can start/stop the SQL Server Browser in SQL Server Express 2022 using:
- SQL Server Configuration Manager (Recommended)
- Windows Services (services.msc)
- Command Prompt (
net start&net stop) - PowerShell (
Start-Service&Stop-Service)
In the next lesson, you will learn how to start the services available in SQL Server .