| Lesson 7 | Enterprise Manager |
| Objective | Use the Enterprise Manager to administer SQL servers. |
Enterprise Manager to administer SQL - Server
To administer SQL Servers and create databases using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) with SQL Server 2022, follow this step-by-step guide. SSMS is a comprehensive tool for database administrators and developers, and version 19.x is the latest compatible with SQL Server 2022.
-
Launch SSMS
- Open SQL Server Management Studio from your Start Menu or desktop shortcut.
-
Connect to the SQL Server Instance
- In the Connect to Server window:
- Server type: Database Engine
- Server name:
localhostor your server name (can be remote or on-premises) - Authentication: Use Windows Authentication or SQL Server Authentication
- Click Connect
- In the Connect to Server window:
-
Administer the SQL Server
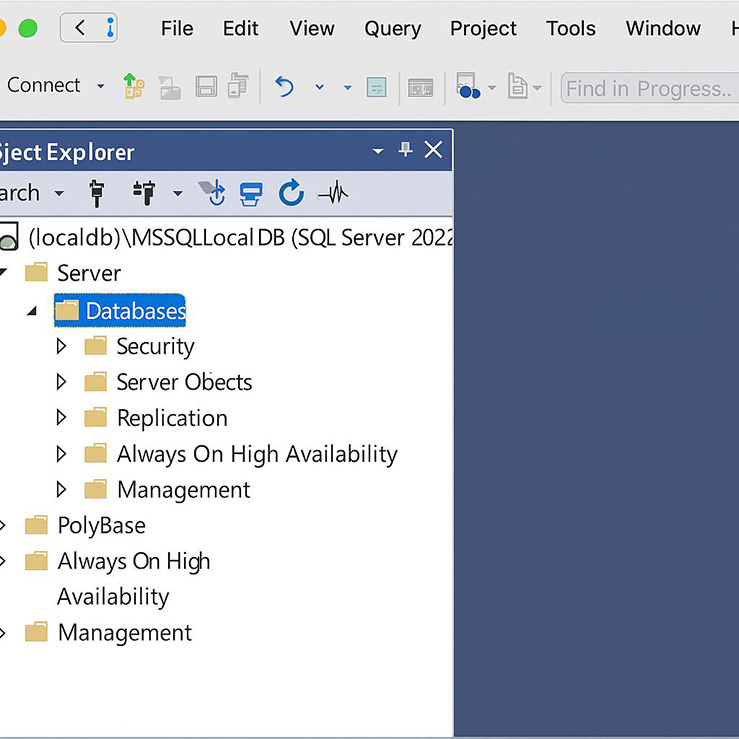
Once connected, the Object Explorer (left pane) shows:
- Databases
- Security
- Server Objects
- Replication
- SQL Server Agent
- Management
You can perform the following administrative tasks:
-
Backup and Restore
- Right-click a database → Tasks > Backup or Restore
- Select options like backup type (Full, Differential, Transaction Log)
-
Manage Security
- Expand Security > Logins
- Right-click Logins → New Login...
- Add Windows or SQL logins and assign roles (e.g.,
db_owner)
-
Monitor Performance
- Expand Management > Activity Monitor
- View live performance metrics (CPU usage, expensive queries, etc.)
Create a New Database
You can create a database using GUI or T-SQL.
-
Using the GUI
- Right-click Databases in Object Explorer → New Database
- Enter a Database name
- Optionally configure:
- Initial size
- Autogrowth
- Filegroups
- Path to .mdf and .ldf files
- Click OK
-
Using T-SQL
- Open a new query window (Click New Query)
- Paste and run:
CREATE DATABASE TimesheetDB ON PRIMARY ( NAME = TimesheetData, FILENAME = 'C:\SQLData\TimesheetData.mdf', SIZE = 10MB, MAXSIZE = 100MB, FILEGROWTH = 5MB ) LOG ON ( NAME = TimesheetLog, FILENAME = 'C:\SQLData\TimesheetLog.ldf', SIZE = 5MB, MAXSIZE = 50MB, FILEGROWTH = 5MB );
Verify Database Creation
- Expand Databases in Object Explorer
- Your new database (e.g.,
TimesheetDB) should appear
Create Tables and Relationships
- Right-click the Tables folder under the new database → New Table
- Define column names, data types, and constraints
- Save the table with a meaningful name
Alternatively, use T-SQL:
USE TimesheetDB;
GO
CREATE TABLE Employees (
EmployeeID INT PRIMARY KEY,
Name NVARCHAR(100),
Role NVARCHAR(50),
HourlyRate DECIMAL(10,2)
);
Run Queries and Test
- Use Query window for SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, JOINs, etc.
SELECT * FROM Employees;
Enable Advanced Features (Optional)
- Configure features like:
- Query Store
- Columnstore Indexes
- Temporal Tables
- Memory-optimized tables
Summary Table
| Task | Where in SSMS |
|---|---|
| Connect to server | Connect to Server dialog on startup |
| Create database | Right-click `Databases` → New Database |
| Write SQL scripts | Toolbar → New Query |
| Create login/user | `Security` → Right-click `Logins` |
| Backup/restore database | `Tasks` on database right-click menu |
| Monitor performance | `Management` → Activity Monitor |
| Configure server settings | Right-click server → Properties |
Create New Objects
In SQL Server 2022, SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) serves as the primary graphical interface for browsing and managing SQL Server objects. SSMS allows you to create, modify, or delete database objects such as tables, views, stored procedures, and indexes directly from the Object Explorer. The interface supports context-sensitive right-click menus, making it easy to perform operations specific to the selected object. For instance, to alter a table, you can either use T-SQL in the Query Editor or right-click the table within Object Explorer and choose the appropriate action from the context menu.Most administrative and development tasks can be efficiently carried out using SSMS’s graphical tools. In the next lesson, you'll learn how to use the Query Editor to write and execute Transact-SQL statements directly.