Lesson 10
SQL Server Overview - Conclusion
This module presented an overview of SQL Server and some of its most useful features and tools. Having completed it, you should now be able to:
- Define a relational database
- Identify and describe SQL Server 2022 services
- Describe SQL Server 2022 architecture
- Plan an effective SQL Server 2022 installation strategy
- Use the Enterprise Manager to administer SQL servers
- Use the Query Analyzer to execute queries and view their results
- Describe some of the most useful wizards available in Microsoft SQL Server 2022
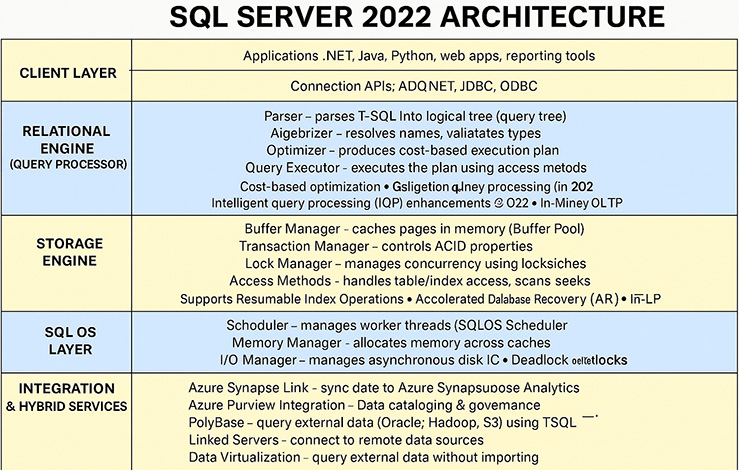
🏗️ SQL Server 2022 Architecture Overview
The SQL Server 2022 Architecture is a layered and modular system designed to manage, store, retrieve, and secure data efficiently across hybrid environments. Below is a structured overview of its architecture, reflecting core components, processes, services, and integrations.
-
Client Layer
- Applications: .NET, Java, Python, web apps, reporting tools
- Communication: TDS (Tabular Data Stream) protocol
- Connection APIs: ADO.NET, JDBC, ODBC, OleDB
- Relational Engine (Query Processor)
- Responsible for query parsing, optimization, and execution.
-
Component Description Parser Parses T-SQL into logical tree (query tree) Algebrizer Resolves names, validates types Optimizer Produces cost-based execution plan Query Executor Executes the plan using access methods - Uses cost-based optimization for execution plans
- Supports intelligent query processing (IQP) enhancements in 2022
- Can call into PolyBase or external sources
- Manages physical storage, indexes, and transaction logs.
-
Subsystem Description Buffer Manager Caches pages in memory (Buffer Pool) Transaction Manager Controls ACID properties Lock Manager Manages concurrency using locks/latches Access Methods Handles table/index access, scans, seeks File System Interface Reads/writes .mdf, .ndf, .ldf files - Supports Resumable Index Operations, Accelerated Database Recovery (ADR), and In-Memory OLTP.
- Abstracts hardware resources for threads, memory, and I/O.
-
Service Role Scheduler Manages worker threads (SQLOS Scheduler) Memory Manager Allocates memory across caches I/O Manager Manages asynchronous disk I/O Deadlock Detection Tracks transaction locks and detects deadlocks
- SQL Server 2022 offers tight Azure integration and external data access features.
-
Feature Role Azure Synapse Link Sync data to Azure Synapse Analytics Azure Purview Integration Data cataloging and governance PolyBase Query external data (Oracle, Hadoop, S3) using T-SQL Linked Servers Connect to remote data sources Data Virtualization Query external data without importing
- Provides authentication, authorization, and data protection.
-
Feature Description Authentication Windows, SQL logins, Azure AD Authorization Role-based access control (RBAC) Encryption TDE, Always Encrypted with secure enclaves Auditing and Row-Level Security Policy-driven data access and logging
-
Technology Description Always On Availability Groups Synchronous/Asynchronous replication Contained Availability Groups Simplified multi-database failover Failover Cluster Instances (FCI) Windows Server Failover Clustering Backup to URL / Azure Blob Cloud-integrated backup options
Glossary terms
This module introduced you to the following terms:
- ad hoc
- API
- console
- context sensitive
- distributed transaction
- gigabytes
- referential integrity
- scheduling
- table
- terabyte
Largest size that can be stored as a column in a Database Table
In SQL Server 2022, the largest size that can be stored in a single column of a database table depends on the data type used. Below is a summary of the maximum sizes for various data types:
🔹 String and Binary Data Types (Variable-length)
🔹 Other Notable Maximums
⚠️ Important Considerations
✅ Summary The largest possible size for a single column is:
🔹 String and Binary Data Types (Variable-length)
| Data Type | Max Size | Notes |
|---|---|---|
VARCHAR(n) |
Up to 8,000 bytes | n max is 8000 unless using MAX |
NVARCHAR(n) |
Up to 4,000 characters | Uses 2 bytes per character (up to 8000 bytes total) |
VARCHAR(MAX) |
Up to 2^31-1 bytes (2 GB) | For large text data (approx 2 GB) |
NVARCHAR(MAX) |
Up to 2^30-1 characters (2 GB) | Unicode text; ~1 GB limit in characters |
VARBINARY(MAX) |
Up to 2^31-1 bytes (2 GB) | Used for large binary data like images or files |
| Data Type | Max Size | Notes |
|---|---|---|
TEXT, NTEXT, IMAGE |
~2 GB | Deprecated, use VARCHAR(MAX), NVARCHAR(MAX), or VARBINARY(MAX) |
XML |
Up to 2 GB | Internally stored as a BLOB |
GEOMETRY, GEOGRAPHY |
2 GB | For spatial data types |
ROWVERSION / TIMESTAMP |
8 bytes | Not datetime-related; used for versioning |
⚠️ Important Considerations
- The maximum size per row in SQL Server is 8,060 bytes (excluding
MAXcolumns). - Columns using
MAXtypes are stored off-row if their content exceeds certain thresholds. - You can have multiple
MAXcolumns, but practical limits depend on performance and storage.
✅ Summary The largest possible size for a single column is:
> 2^31 - 1 bytes (2,147,483,647 bytes ≈ 2 GB) …for `VARCHAR(MAX)`, `NVARCHAR(MAX)`, or `VARBINARY(MAX)`.
SQL Server Overview - Quiz
Before moving on to the next module, click the Quiz link below on the left to check your knowledge of the information covered in this module.
SQL Server Overview - Quiz
SQL Server Overview - Quiz