| Lesson 3 | Tuning considerations of the shared pool |
| Objective | Describe the operation of the shared pool. |
Tuning considerations of Shared Pool
The size of the various components within the SGA, including the Shared Pool, can be adjusted according to the specific requirements of the database and the performance characteristics of the applications accessing it.
The SGA consists of several structures, among which are the Database Buffer Cache, the Shared Pool, the Redo Log Buffer, and the Java Pool, among others. Each of these components can be dynamically sized, and their size does not follow a strict hierarchical order. The Database Buffer Cache is often the largest component of the SGA because it is used to cache blocks of data retrieved from the database. The size of the Database Buffer Cache can have a significant impact on database performance, and it is usually tuned to be as large as possible within the constraints of the available system memory.
The Shared Pool, on the other hand, is used to store shared memory constructs such as SQL statements, PL/SQL code, and dictionary cache data. Its size can also impact database performance, particularly in systems with a high degree of SQL or PL/SQL execution.
Therefore, while the Shared Pool can be a large component of the SGA, it is not necessarily the second largest. The sizes of the various SGA components should be determined based on a careful analysis of the specific performance requirements and characteristics of the database and its associated applications. Overall, the correct tuning of the Oracle instance involves a comprehensive understanding of the workload characteristics, system resources, and business requirements, along with a thorough knowledge of the behavior and configuration options of the Oracle Database software. The aim is to balance the allocation of memory among the various SGA components to achieve optimal system performance.
The SGA consists of several structures, among which are the Database Buffer Cache, the Shared Pool, the Redo Log Buffer, and the Java Pool, among others. Each of these components can be dynamically sized, and their size does not follow a strict hierarchical order. The Database Buffer Cache is often the largest component of the SGA because it is used to cache blocks of data retrieved from the database. The size of the Database Buffer Cache can have a significant impact on database performance, and it is usually tuned to be as large as possible within the constraints of the available system memory.
The Shared Pool, on the other hand, is used to store shared memory constructs such as SQL statements, PL/SQL code, and dictionary cache data. Its size can also impact database performance, particularly in systems with a high degree of SQL or PL/SQL execution.
Therefore, while the Shared Pool can be a large component of the SGA, it is not necessarily the second largest. The sizes of the various SGA components should be determined based on a careful analysis of the specific performance requirements and characteristics of the database and its associated applications. Overall, the correct tuning of the Oracle instance involves a comprehensive understanding of the workload characteristics, system resources, and business requirements, along with a thorough knowledge of the behavior and configuration options of the Oracle Database software. The aim is to balance the allocation of memory among the various SGA components to achieve optimal system performance.
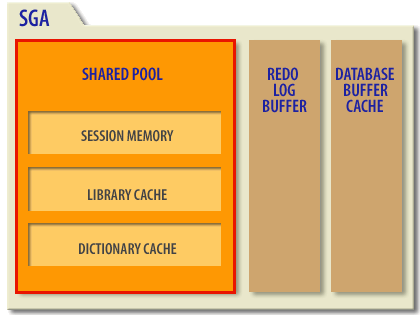
Oracle Shared Pool
Library cache
The library cache stores the plan information for SQL that is currently being executed. This area also holds stored procedures and trigger code. The SQL areas within the library cache hold SQL so that a repeated SQL statement does not need to be re-parsed each time that the SQL is processed.
Data Dictionary Cache
The data dictionary cache stores environmental information, including referential integrity, table definitions, indexing information, and other metadata stored within Oracle's internal tables. When a package is invoked, Oracle first checks the dictionary cache to see if the package is already in memory. This eliminates disk access and therefore performance of SQL statements improves. Later in the course, you will learn to query the dictionary cache to compare dictionary cache hits to misses.
Session Information
The session information area stores session information for systems that are using Oracle Net Services on Oracle Shared Server.
For systems that do not use Oracle Shared Server, this area will not use much space.
Sizing the Shared Pool
One of the confounding problems with Oracle is that all of these sub-areas are sized by only one
In the following lessons, you will get an overview of the tuning issues involved in each of the major components of the shared pool, the library cache, the data dictionary cache and the session information area. Let bus egin with the library cache.
init.ora parameter called shared_pool_size. It is impossible to dedicate separate regions of memory for the components within the shared pool.In the following lessons, you will get an overview of the tuning issues involved in each of the major components of the shared pool, the library cache, the data dictionary cache and the session information area. Let bus egin with the library cache.