| Lesson 5 | The redo log buffer |
| Objective | Explain the Function of the Redo Log Buffer |
Function of Oracle Redo Log Buffer
The redo log buffer is an area of memory set aside to hold redo log entries long enough for the Log Writer process to write them to the redo log files. Ideally, the log writer would write the redo log as fast as new entries were generated. Then you would not need a buffer. In reality, that's simply not feasible. This following series of images shows conceptually how the redo log buffer is used:
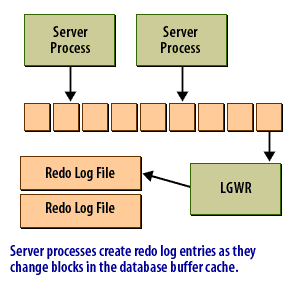
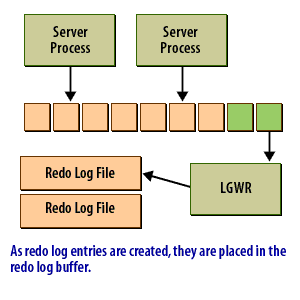
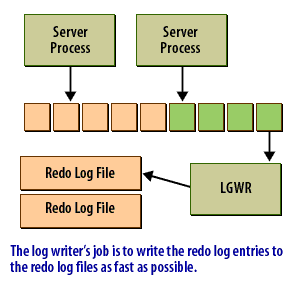
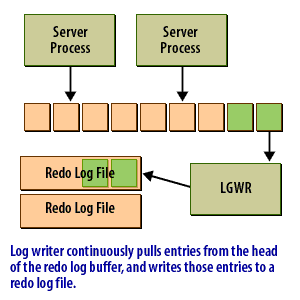
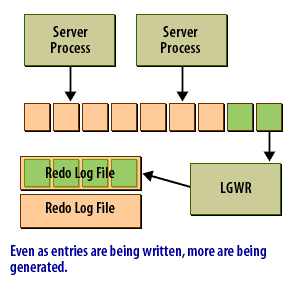
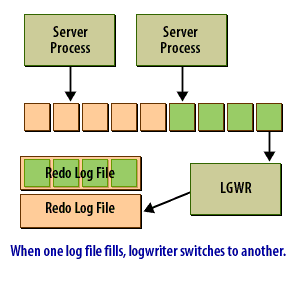
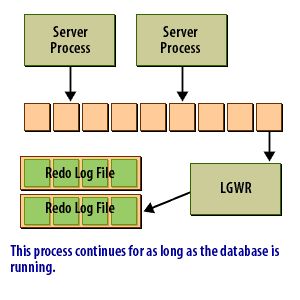
Data in the redo log buffer when an Oracle Instance crashes
When an instance crashes in an Oracle database, the data in the redo log buffer is lost because the redo log buffer resides in the system's volatile memory (RAM). However, Oracle uses a mechanism called "redo log files" to safeguard the database's transactional integrity and durability.
Here’s what happens:
Thus, even though the redo log buffer itself is lost, the persistent redo log files ensure that no committed transactions are lost, and the database can be recovered to a consistent state.
Here’s what happens:
- Redo Log Files: Oracle continuously writes redo entries from the redo log buffer to the redo log files on disk, which are non-volatile storage. These redo log files ensure that all changes made to the database can be recovered.
- Checkpoint Process: Periodically, Oracle performs a checkpoint, which ensures that all modified data blocks in the database buffer cache are written to the data files on disk. This checkpoint also records the position in the redo log file up to which all changes are guaranteed to be saved to the disk.
- Instance Recovery: Upon instance recovery, Oracle uses the redo log files to apply any changes that were recorded in the redo logs but not yet written to the data files at the time of the crash. The Oracle recovery process reads the redo log files from the last checkpoint and reapplies all the changes to bring the database to a consistent state.
Thus, even though the redo log buffer itself is lost, the persistent redo log files ensure that no committed transactions are lost, and the database can be recovered to a consistent state.
Redo log buffer
The redo log buffer caches redo information until it is written to the physical redo log files stored on a disk. This buffer also improves performance. Oracle caches the redo until it can be written to a disk at a more optimal time, which avoids the overhead of constantly writing the redo logs to disk.
The redo log buffer holds the most recent changes to the data blocks in the datafiles. When the redo log buffer is one-third full, or every three seconds, Oracle writes redo log records to the redo log files. As of Oracle 10g, the LGWR process will write the redo log records to the redo log files when 1MB of redo is stored in the redo log buffer. The entries in the redo log buffer, once written to the redo log files, are critical to database recovery if the instance crashes before the changed data blocks are written from the buffer cache to the datafiles. A user's committed transaction is not considered complete until the redo log entries have been successfully written to the redo log files.
The redo log buffer holds the most recent changes to the data blocks in the datafiles. When the redo log buffer is one-third full, or every three seconds, Oracle writes redo log records to the redo log files. As of Oracle 10g, the LGWR process will write the redo log records to the redo log files when 1MB of redo is stored in the redo log buffer. The entries in the redo log buffer, once written to the redo log files, are critical to database recovery if the instance crashes before the changed data blocks are written from the buffer cache to the datafiles. A user's committed transaction is not considered complete until the redo log entries have been successfully written to the redo log files.
SGA - Memory Structures - Quiz
Click the Quiz link below to test how well you've learned the material so far.
SGA - Memory Structures - Quiz
SGA - Memory Structures - Quiz