| Lesson 2 | Overview of Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) |
| Objective | Capabilities of the Oracle Enterprise Manager. |
Capabilities of Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) in Oracle 23c
Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) has evolved significantly by the time of Oracle 23c.
Its role is broader, deeper, and much more cloud-aware compared to earlier versions.
Here is a detailed breakdown:
Here is a detailed breakdown:
-
Complete Lifecycle Management for Databases (On-Premises and Cloud)
- Provisioning: Automates database creation for Oracle 23c across bare metal, VMs, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).
- Patching: Streamlined patch management with automation (including Fleet Patching and Provisioning — FPP).
- Upgrades: Guided upgrade paths, compatibility checks, and auto-corrective actions when upgrading to 23c.
- Backup and Recovery: Deep integration with Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) for backup strategies and disaster recovery.
- Cloning: Database cloning (both full and snapshot) for dev/test environments.
-
Advanced Monitoring and Performance Diagnostics
- Real-Time SQL Monitoring: Tracks SQL execution for bottlenecks.
- ASH and AWR Integration: Active Session History (ASH) and Automatic Workload Repository (AWR) diagnostics built-in.
- Automatic Database Diagnostics Monitor (ADDM): Diagnoses performance issues and suggests corrective actions for Oracle 23c databases.
- Top Activity, Blocking Sessions, Wait Event Analysis: Visuals and reports.
-
Multitenant and Sharding Management
- CDB/PDB Management: Native support for multitenant architecture — manage container databases (CDBs) and pluggable databases (PDBs) easily.
- PDB Lifecycle Operations: Plug, unplug, relocate PDBs across servers.
- Sharding: Visualize and manage Oracle Sharded databases introduced strongly by Oracle 12c and now matured in 23c.
-
Security and Compliance
- Unified Audit Trail Monitoring: Audit activity across multiple databases.
- Database Security Assessment Tool (DBSAT) integration: Assesses security posture of Oracle 23c databases.
- Data Masking and Subsetting: Helps meet GDPR, CCPA, and other compliance standards.
- Privileged User Access Monitoring: Track sensitive access activities.
- Database Vault and Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) management.
- SQL Tuning Advisor: Suggests indexes, rewrites SQL, and recommends optimizer statistics refresh.
- Automatic Indexing: Monitors, tests, and creates indexes automatically (leveraging Oracle 23c’s enhanced auto-indexing features).
- Anomaly Detection: Uses ML models to detect abnormal database behavior.
- Capacity Planning: Predicts storage, CPU, and memory needs based on historical patterns.
- Hybrid Cloud Support: Manage on-premises, private cloud, and Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) environments together from a single console.
- Autonomous Database Management: Monitor Autonomous Database instances (23c autonomous editions) alongside traditional DBs.
- Database Fleet Management: Mass monitor, patch, and upgrade hundreds/thousands of databases simultaneously.
- Business-Driven Monitoring: Monitor applications based on service-level objectives (SLOs).
- Application-to-Database Mapping: Understand how slowdowns in the database affect applications.
- Extend OEM 23c capabilities by adding plugins for:
- Oracle Middleware
- Oracle Applications (e.g., EBS, PeopleSoft)
- Non-Oracle systems (SQL Server, AWS RDS, SAP HANA)
- New HTML5 Interface: Fully web-based, no reliance on Flash or Java applets.
- RESTful APIs: Automate management and monitoring tasks programmatically using REST.
- Command Line (EMCLI): Still available for bulk operations and scripting.
Summary Table
| Category | Oracle Enterprise Manager 23c Capabilities | |
|---|---|---|
| Lifecycle Management | Provisioning, Patching, Backup, Upgrades, Cloning | |
| Performance Monitoring | Real-time SQL, AWR, ADDM, Wait Events | |
| Multitenant/Sharding | Manage CDBs/PDBs, Sharded Databases | |
| Security | Auditing, TDE, Data Masking, Security Assessment | |
| Machine Learning | Auto Indexing, SQL Tuning, Anomaly Detection | |
| Cloud | Hybrid Management (On-prem + OCI + Autonomous DB) | |
| Service Levels | App-to-DB Mapping, SLA Monitoring | |
| Extensibility | Plugin System, REST APIs, EMCLI |
Key Point: Oracle Enterprise Manager 23c is no longer just a DBA tool, it is a complete database, cloud, security, and compliance operations platform.
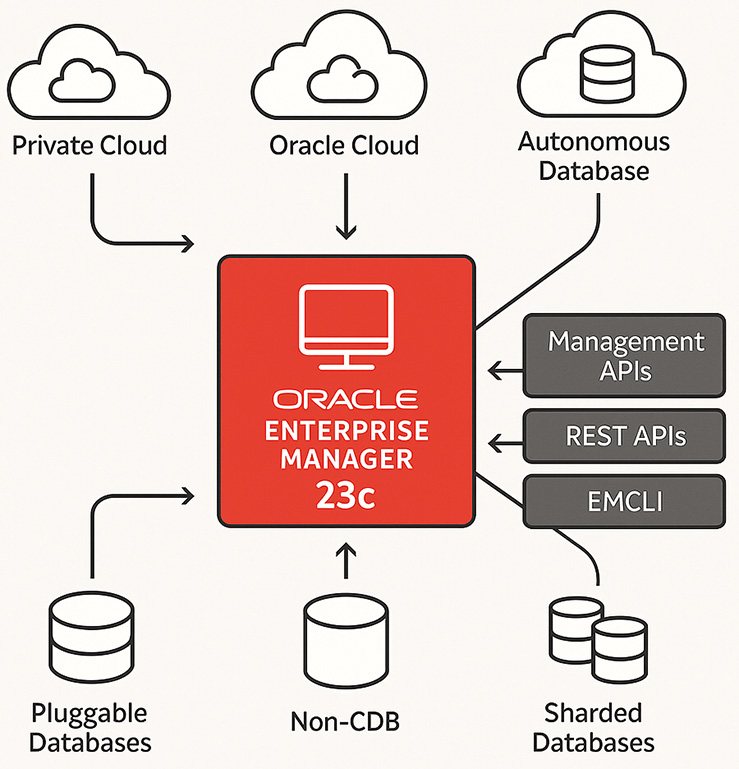
From this central box:
-
Upward connections go to three cloud-related components:
- Private Cloud (left)
- Oracle Cloud (center)
- Autonomous Database (right)
-
Downward connections go to three types of databases:
- Pluggable Databases (left)
- Non-CDB (center)
- Sharded Databases (right)
-
To the right side, three horizontal arrows point outward to:
- Management APIs
- REST APIs
- EMCLI (Enterprise Manager Command Line Interface)
Summary of Relationships:
- OEM 23c manages traditional, multitenant, and sharded databases.
- OEM 23c integrates with both on-premises (Private Cloud) and Oracle Cloud environments, including Autonomous Databases.
- OEM 23c exposes APIs and a command-line interface for automation and external management.
How Operations would flow step-by-step through Oracle 23c
How operations happen step-by-step through the Oracle Enterprise Manager 23c diagram.
OEM 23c Operations Flow
Summary View
OEM 23c Operations Flow
-
Monitor
- Continuously monitor health and performance of:
- Traditional Databases (Non-CDBs)
- Pluggable Databases (PDBs within CDBs)
- Sharded Databases
- Private Cloud and Oracle Cloud (including Autonomous Databases)
- Continuously monitor health and performance of:
-
Diagnose
- Detect performance issues via:
- Real-Time SQL Monitoring
- AWR and ASH Reports
- Anomaly Detection (Machine Learning models)
- Detect performance issues via:
-
Manage
- Perform lifecycle operations:
- Provision and Clone Databases
- Apply Patches and Upgrades
- Backup and Restore
- Manage Resource Allocation (CPU, Memory, Storage)
- Perform lifecycle operations:
-
Secure
- Enforce security measures:
- Unified Auditing
- Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
- Privileged User Access Control
- Compliance Reporting (e.g., GDPR, CCPA)
- Enforce security measures:
-
Automate
- Execute management tasks using:
- Management APIs (REST, EMCLI)
- Autonomous Features (e.g., Auto Indexing, Auto Patching)
- Scheduled Jobs and Fleet Operations
- Execute management tasks using:
-
Report and Optimize
- Generate insights and optimization suggestions:
- Capacity Planning Reports
- SQL Tuning Recommendations
- Service Level Agreement (SLA) Monitoring for Applications
- Generate insights and optimization suggestions:
Summary View
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Monitor health and environment |
| 2 | Diagnose performance or security issues |
| 3 | Manage database lifecycle tasks |
| 4 | Secure databases and cloud environments |
| 5 | Automate repetitive operations |
| 6 | Report on KPIs and optimize performance |
Describe the capabilities of the Oracle Enterprise Manager.
Oracle Enterprise Manager is a system-management tool that provides an integrated solution for managing your heterogeneous database environment. It combines a graphical console, agents, common services, and tools to provide an integrated, comprehensive systems-management platform for managing Oracle products. From the Oracle Enterprise Manager console, you can:
- Administer, diagnose, and tune multiple databases
- Distribute software to multiple servers and clients
- Schedule jobs on multiple nodes at varying time intervals
- Monitor objects and events throughout the network
- Customize your display using multiple graphic maps and groups of network objects such as nodes and databases
- Administer Oracle Parallel Servers (For information about administering Oracle Parallel Servers, see the Oracle documentation: Oracle Parallel Server Support for the Oracle Enterprise Manager Console Guide.)
Oracle Enterprise Manager 11g Features
Oracle Enterprise Manager (OEM) has introduced a few new 11g management features into the OEM GUI interface.
The most prominent 11g OEM new features include:
The most prominent 11g OEM new features include:
- Interface OEM to Foreign 3rd party Applications in 11g, OEM interfaces to Siebel and PeopleSoft Corp. into a single platform.
- OEM Easy de-install: In 11g, OEM will uninstall both successful and unsuccessful Oracle installs.
- OEM MOSC Support workbench: In 11g, OEM interfaces directly with My Oracle Support Community (MOSC), formally MetaLink.
Once the Automatic Diagnostic Repository (ADR) has detected and reported a critical problem, the DBA can interrogate the ADR, report on the source of the problem, and in some cases even implement repairs. - Database repair wizard: A GUI to guide beginners through the steps to diagnose and repair Oracle issues.
- Better OEM Grid tools: Another new Oracle11g feature may be improved RAC and Grid monitoring, especially on the cache fusion interconnect.
- Improved Database Home Page
- Performance changes
- Integrated Interface for LogMiner
- Advanced Replication Interface
- Wait Activity Detail Enhancement
- Easy Oracle Text Management
- Clone Database
- Migrate Database to ASM: Oracle 11g OEM has a utility to allow fast migration of data files into ASM.
- OEM Workspace Manager