| Lesson 5 | Oracle Internet Directory |
| Objective | Describe the Oracle Internet Directory and what it can do. |
Oracle Internet Directory
Oracle 8i introduced the Oracle Internet Directory. Which version of Oracle RDBMS phased out "Oracle Internet Directory"?
The Oracle Internet Directory (OID) has not been fully phased out from Oracle's product line, but its usage and emphasis have significantly declined in favor of more modern and cloud-compatible identity services.
📜 Historical Timeline of Oracle Internet Directory (OID)
✅ Final Notes
OID is not officially deprecated as of Oracle 23c, but it is:
* For new deployments, Oracle recommends using IDCS or OUD, especially for integration with:
🚨 Conclusion:
Oracle 23c effectively phases out Oracle Internet Directory in favor of more modern, scalable, and cloud-native directory solutions—but OID is still available for legacy support.
📜 Historical Timeline of Oracle Internet Directory (OID)
| Oracle RDBMS Version | Status of OID | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Oracle 8i (1999) | ✅ Introduced | LDAP v3-compliant directory service used for storing user identities and DB configurations. |
| Oracle 9i – 11g | ✅ Actively supported | Widely used with Enterprise User Security and Oracle Identity Management. |
| Oracle 12c | ✅ Supported but de-emphasized | Oracle promoted Oracle Unified Directory (OUD) for new deployments. |
| Oracle 18c / 19c | ⚠️ Still supported but aging | Marked as legacy in many deployment architectures. |
| Oracle 21c | ⚠️ Available but not enhanced | Oracle Identity Cloud Service (IDCS) takes precedence. |
| Oracle 23c / 23ai | ❌ Not a core component | OID is no longer promoted, and new identity integrations rely on IDCS, OUD, or OAuth 2.0/OIDC providers. |
✅ Final Notes
OID is not officially deprecated as of Oracle 23c, but it is:
- No longer actively developed for cloud-native environments.
- Not included in most modern cloud-enabled Oracle RDBMS stacks.
- Superseded by:
- Oracle Identity Cloud Service (IDCS)
- Oracle Unified Directory (OUD)
* For new deployments, Oracle recommends using IDCS or OUD, especially for integration with:
- Autonomous Database
- OCI IAM
- Federation via OAuth2 / SAML / OpenID Connect
🚨 Conclusion:
Oracle 23c effectively phases out Oracle Internet Directory in favor of more modern, scalable, and cloud-native directory solutions—but OID is still available for legacy support.
In a continuing effort to fully integrate Oracle with the Internet, Oracle has introduced a new product called the Internet Directory. The development of the Oracle Internet Directory stems from an earlier product called OracleOffice.
This tool comes as part of Oracle's Enterprise Edition (release 8.1.6 and higher).
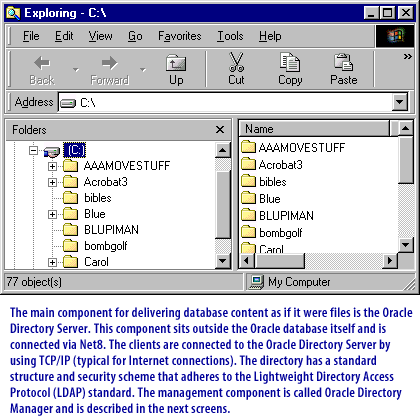
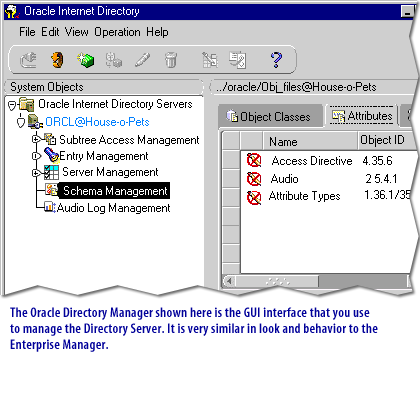
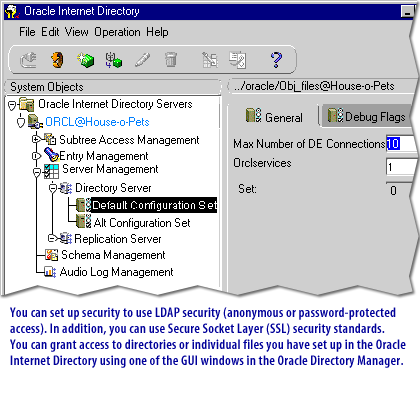
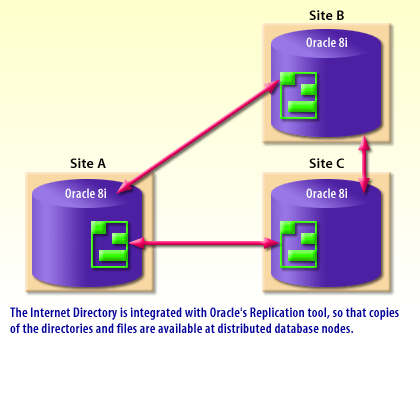
The Oracle Internet Directory tool lets you store all your database data in a file system that is accessible to your users just like any other files. For example, your sales representative can open and view a file of customers using his favorite text editor even though the customer data resides in the database. Without Internet Directory, your sales representative would have to write an SQL query, or ask you to write it for him, in order to access the file. Look through the slide show below to see how the Internet Directory works.
The Oracle Internet Directory tool lets you store all your database data in a file system that is accessible to your users just like any other files. For example, your sales representative can open and view a file of customers using his favorite text editor even though the customer data resides in the database. Without Internet Directory, your sales representative would have to write an SQL query, or ask you to write it for him, in order to access the file. Look through the slide show below to see how the Internet Directory works.
For Oracle 23c and 23ai
The possibilities for leveraging Oracle 23c's advanced features are extensive. Here are some ideas:
- Build dynamic web applications that present database table data using RESTful APIs, JSON Duality Views, or GraphQL. These APIs can be indexed by modern web crawlers and integrated with search platforms.
- Enable content authors to interact with database content via HTTPS-based REST endpoints. Developers can retrieve and update structured or unstructured data through secure interfaces, compatible with modern editors and tools.
- Store and manage images and rich media as external files in Oracle Cloud Object Storage or in BLOB columns, allowing direct integration with tools like Photoshop. Metadata and access controls remain queryable through the database.
- Expose database content securely for download via Oracle REST Data Services (ORDS) or OCI object URLs, allowing end users to retrieve structured data over HTTP(S) or through secure API gateways.
- Integrate with modern identity services (e.g., Oracle Identity Cloud Service, OAuth2, or OpenID Connect) for secure access, replacing the legacy directory-based authentication provided by Oracle Internet Directory.
Modern Technologies Replacing OID Use Cases
| Legacy Functionality (OID) | Oracle 23c / 23ai Modern Equivalent |
|---|---|
| LDAP-based access to DB metadata | Oracle Cloud Infrastructure IAM / IDCS |
| File-like access to DB data | REST APIs via ORDS / Autonomous Database |
| Web-accessible tables and queries | JSON Relational Duality Views / APEX / REST services |
| Image/file management within database | BLOBs + OCI Object Storage + Secure Metadata Tables |
| FTP access to DB content | HTTPS/REST endpoints or pre-authenticated OCI URLs |
Oracle internet Directory - Exercise
Click here to practice designing a strategy for directories and files.
Oracle Internet Directory - Exercise
The next lesson describes some of the other tools and technologies Oracle offers.
Oracle Internet Directory - Exercise
The next lesson describes some of the other tools and technologies Oracle offers.