Lesson 8
Oracle Network Services Summary
This module introduced you to the features of Oracle Network Services.
You should now be able to:
You should now be able to:
- Identify features of the Oracle Net listener
- Describe Oracle enhancements for scalability
- Identify the characteristics for partitioned tables
- Describe Oracle enhancements and features that improve connectivity
- Describe Oracle enhancements that improve manageability of network/database tasks
- Describe Oracle enhancements that improve and simplify security
Oracle Network Services beginning with Oracle 9i
Oracle Network Services, beginning with Oracle 9i, appear to have introduced several features aimed at enhancing network security, scalability, and manageability. These features might include:
- Advanced Security: Oracle 9i potentially introduced more robust security features, such as stronger encryption algorithms and support for SSL/TLS. This could have been designed to ensure secure data transmission across networks.
- Scalability and Performance Improvements: There might have been significant enhancements in scalability, possibly including features like connection pooling and shared server configurations. These would be intended to handle a large number of client connections more efficiently.
- Load Balancing and Failover Capabilities: Oracle 9i may have improved its support for load balancing and failover, which would be crucial for high availability and reliability. This could involve distributing client requests across multiple servers and providing automatic failover in case of server failure.
- Enhanced Configuration and Management Tools: The introduction of better management tools could have been a focus, possibly simplifying the configuration and management of network components. This would include user-friendly interfaces and command-line tools.
- Integration with Directory Services: There might have been integration with directory services like LDAP, which would allow centralized management of network resources and user authentication.
- Support for Multiple Network Protocols: Oracle 9i potentially expanded its support for various network protocols, ensuring compatibility and flexibility in different network environments.
- Monitoring and Diagnostics Enhancements: Enhanced monitoring and diagnostic tools could have been included to provide detailed insights into network performance and to quickly identify and resolve network-related issues.
Oracle Networking Concepts
The following paragraph discusses "Oracle Network Services" functions with the tools that are used to implement those functions. Primary Communication Foundations for an Oracle database are:- Oracle's Family of Networking Features:
The Network Configuration Files consist of:
- sqlnet.ora: a) Main Oracle Net configuration file, b) On both Client and Server
- listener.ora: a) Configuration for the Net Listener, b) On Server only
- tnsnames.ora:
- Contains the Connect Name to descriptor mappings,
- Used by the TNSNames Naming adapter,
- On both the client and server.
- ldap.ora: a) Contains LDAP configuration information, b) Used the LDAP Naming adapter, c) On both the Client and Server
| Security | RADIUS |
| Connectivity | Multiplexing |
| Manageability | Shared repository |
| Partitioning | Row movement |
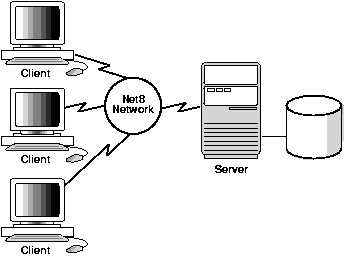
Network services enables services and their applications to reside on different computers and communicate as peer applications.
The main function of Net is to establish network sessions and transfer data between a client machine and a server or between two servers. Net is located on each machine in the network and once a network session is established, Net acts as a data courier for the client and the server.
The main function of Net is to establish network sessions and transfer data between a client machine and a server or between two servers. Net is located on each machine in the network and once a network session is established, Net acts as a data courier for the client and the server.
Database Connection Features
The connection between the client and the database server is a key component of the overall architecture. The database connection is responsible for supporting all communications between an application and the data it uses. Oracle includes a number of features that establish and tune your database connections. We have divided the discussion into two categories:
- database networking and
- Oracle Application Server.
Database Networking
Database users connect to the database by establishing a network connection. You can also link database servers via network connections. Oracle provides a number of features to establish connections between users and the database and/or between database servers, as described in the following subsections.
Glossary
In this module, you were introduced to the following glossary terms:
The next module covers the changes in Net installation and configuration.
- Advanced Queuing: A pre-defined package enabling you to store messages into queues for deferred retrieval and processing by the Oracle server.
- Cache fusion: A diskless data transfer method for Oracle Parallel Server (OPS) that moves information from the cache of one database instance to the cache of another database instance.
- Multiplexing: Combining several individual transmissions and sending them across a single connection to and from a database.
- Partitioned table: A table containing data in multiple physical tables. This divides large amounts of data into smaller segments.
- RADIUS: Acronym for Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service, a client-server security protocol that is used primarily with the Internet.
- Snapshot: A replica of a table or part of a table that resides on another database instance. Snapshots can be read-only or updateable.
- Transparent application failover (TAF) : A feature in Net to seamlessly move a user’s session from one instance to another when the original instance fails.
The next module covers the changes in Net installation and configuration.
Ad Oracle Integration Cloud Service