Lesson 6
Access Database Interface Summary
Microsoft Access interface and the Database window. You have also learned how to open a database and create a new database using a template. And should you have questions, you know how to use Access online Help to answer them.
To create a new database using a template in Microsoft Access 365, follow these steps:
✅ Step-by-Step Guide:
🧠 Tips:
To create a new database using a template in Microsoft Access 365, follow these steps:
✅ Step-by-Step Guide:
- Open Microsoft Access 365
- Launch Access from your Start menu or desktop shortcut.
- Choose a Template
- On the Home screen, you’ll see a list of available templates (e.g., Contact Management, Task Management, Event Planner, Student Database).
- You can also search for templates online using the search bar at the top.
- Select a Template
- Click on the template you want to use.
- A preview window will open with a description and sample thumbnail.
- Name Your Database
- In the File Name box at the bottom of the preview window, enter a name for your new database.
- You can also click the folder icon to change the location where it will be saved.
- Create the Database
- Click the Create button.
- Access will generate a new database file based on the selected template.
- Enable Content (if prompted)
- If the template includes macros or custom forms, you may see a Security Warning. Click Enable Content if you trust the source.
🧠 Tips:
- Templates come with pre-built tables, forms, queries, and reports.
- You can customize the database structure after it's created, just like any other Access database.
Microsoft Access Window interface has been replaced with the Navigation Pane
While the "Database Window" as a separate entity was more prominent in earlier versions of Microsoft Access,
its core functionalities are now integrated into the main Access application window, primarily through the Navigation Pane.
Therefore, the primary elements that constitute this integrated database management area are:
- Navigation Pane: This is the most crucial element for interacting with your database objects. It's typically located on the left side of the Access window and displays a list of all the objects in your database, such as tables, queries, forms, reports, macros, and modules. You use it to open, manage, and organize these objects.
- Object Tabs/Document Window: When you open a database object (like a table, form, or report), it appears in the main work area as a tabbed document (if you have tabbed documents enabled in Access options). This area displays the data or design of the selected object, allowing you to interact with it.
- Ribbon: Located at the top of the Access window, the Ribbon is the primary command bar. It's organized into tabs (e.g., File, Home, Create, External Data, Database Tools) that contain groups of related commands for working with your database and its objects. The specific tabs and commands available change depending on the object you have selected.
- Status Bar: Situated at the very bottom of the Access window, the Status Bar provides information about the current operation, the selected object, or any warnings. It often displays helpful tips as you navigate and work within Access.
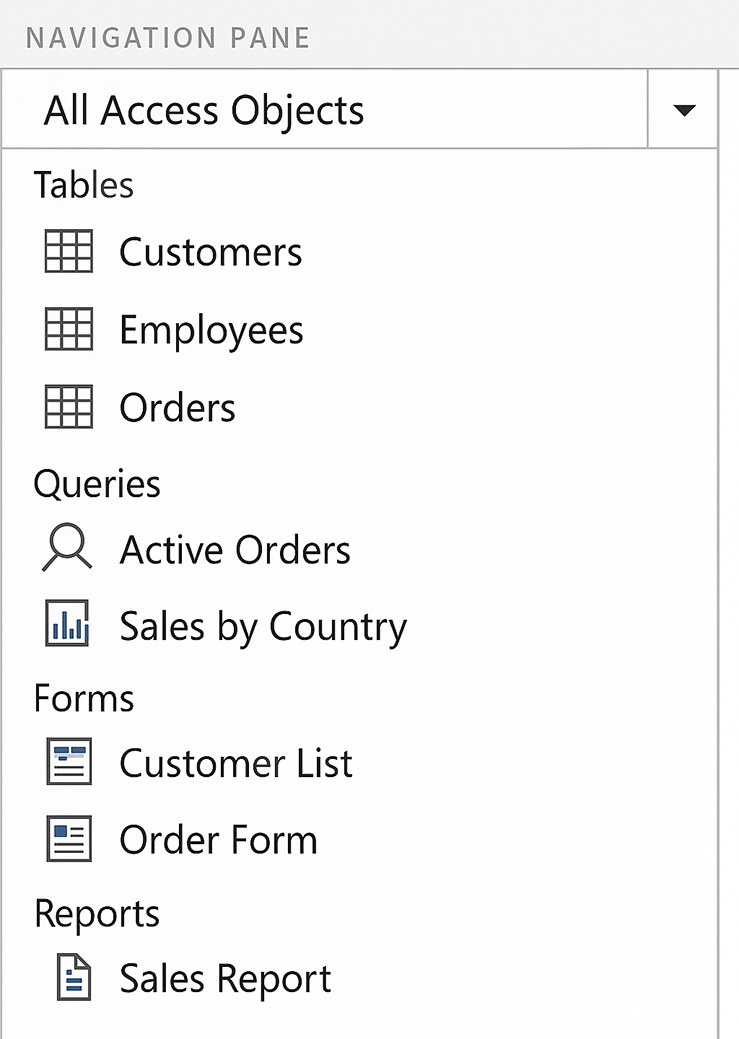
- Tables: Lists relational tables like `Customers`, `Employees`, and `Orders`.
- Queries: Displays saved queries such as `Active Orders` and `Sales by Country`.
- Forms: Provides user-friendly input interfaces like `Customer List` and `Order Form`.
- Reports: Shows formatted output tools, such as `Sales Report`, used for printing and analysis.
Key Functions:
- Object Access: Double-clicking an item opens it in the main workspace.
- Organization: Objects are grouped by type and can be filtered by custom categories or object type.
- Management: Right-clicking an object allows actions such as renaming, deleting, or exporting.
It replaces the legacy "Database Window" and is critical for navigating and organizing the components of a relational database in Access 365.
Terms and Concepts
This module introduced you to the following terms and concepts:
In the next module you will learn more about what a database is, I will introduce some of the terminology you will see throughout the course, and you will learn how to create a database from scratch.
- Database: A database is an organized collection of related data that is stored and accessed electronically. In Access, it is a single file that can contain tables, queries, forms, reports, and other objects used to manage and manipulate information.
- Database Window: The database window (though not a separate window in recent versions, its functionality is within the main Access interface) is the central area from which you view and manage all the objects within your open database. It allows you to open, create, and organize tables, queries, forms, reports, macros, and modules.
- Status Bar: The status bar is a horizontal bar located at the bottom of the Access window that displays information about the current operation, selected object, or warnings. It often provides helpful tips and details as you work within the application.
- Objects: Objects are the fundamental building blocks of an Access database, each designed for a specific purpose. The main types of objects include tables for storing data, queries for retrieving and manipulating data, forms for user interfaces, and reports for presenting data.
- Table: A table is the foundation of a database, organized into rows (records) and columns (fields) to store specific pieces of information about a particular subject. Each row represents a single entity, and each column represents an attribute of that entity.
- Query: A query is a request for specific data from one or more tables in a database, allowing you to filter, sort, calculate, and combine information based on defined criteria. Queries enable you to extract meaningful insights from the raw data stored in your tables.
- Form: A form is a user-friendly interface that allows you to enter, edit, and display data from tables or queries in a controlled and organized manner. Forms simplify data management and improve the user experience compared to directly working with tables.
- Report: A report is a formatted and organized presentation of data from tables or queries, designed for printing or distribution. Reports allow you to summarize, group, and calculate data to communicate information effectively.
- Data: Data refers to the individual facts, figures, details, or statistics that are stored and organized within a database. It is the raw material that database objects are designed to manage, analyze, and present in a meaningful way.
In the next module you will learn more about what a database is, I will introduce some of the terminology you will see throughout the course, and you will learn how to create a database from scratch.
Access Database Review - Quiz
Before we move on, take a multiple-choice quiz to help you determine if you have learned the lessons in this module.
Access Database Review - Quiz
Access Database Review - Quiz