| Lesson 7 | Using stored scripts |
| Objective | Use the run command. |
Using Stored Scripts in Oracle
In the previous lesson, you learned about managing stored scripts within Recovery Manager. This lesson introduces you to the
When the
run command, which is used to execute stored scripts. In addition, the run command allows you to execute operating system commands and SQL commands. When the
run command operates, two things happen. The commands are compiled into blocks or steps of PL/SQL code. Then, these steps are then stored in memory and executed. The compiled version of your script is not stored for later use. Take a look at some samples of the run command in the following series of images below:
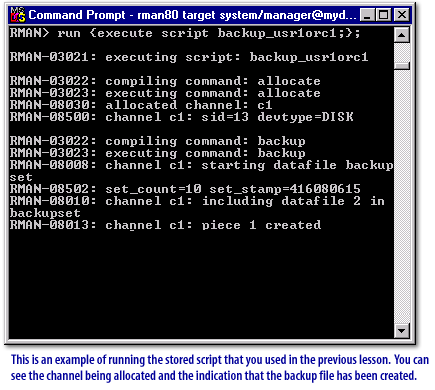
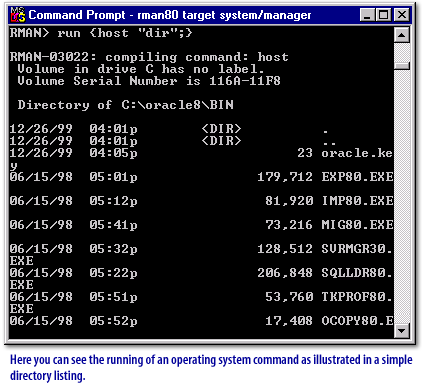
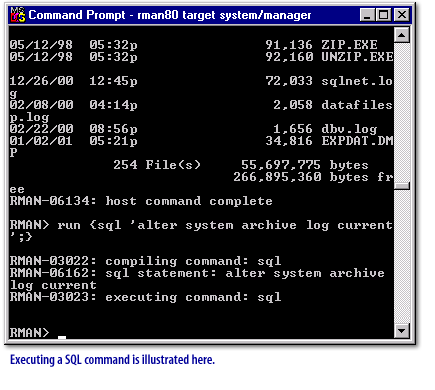
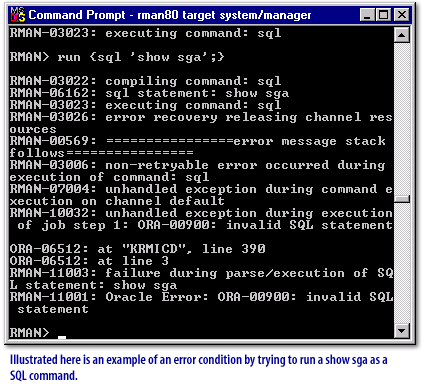
Types of Recovery Manager Commands
RMAN uses two basic types of commands:
- stand-alone commands and
- job commands.
run {
allocate channel c1 type 'sbt_tape';
restore database;
recover database;
}
Stand-Alone Commands
Unlike job commands, stand-alone commands do not appear as sub-commands within run. Following are some of the commands that can appear by themselves: catalog- change
- create catalog, drop catalog, upgrade catalog
- create script, delete script, replace script
- crosscheck
- delete expired backupset
- list
- report
Some of these commands are not strictly stand-alone, however, because they must be preceded by an allocate channel for maintenance command.
Purpose of run command
To compile and execute job commands, which are one or more statements executed within the braces of run. The run command compiles the list of job commands into one or more job steps and then executes them immediately. RMAN compiles and executes each command before processing the next one.
Requirements
- Execute this command only at the RMAN prompt.
- You must precede and follow the list of job commands with an opening and closing brace
Refer to individual entries for information about commands that you can run from the RMAN prompt.
It should be noted that you could use the
run command to execute the same syntax that you might have in a stored script. Below is an example of using the run command to back up the USER_DATA tablespace.
run{
allocate channel 1 type disk;
backup
incremental level = 0
format 'd:\backup\orc1_%s_%p'
(tablespace 'user_data');
};
In the next lesson, you will learn what data dictionary views are available to you to interrogate the recovery catalog.