| Lesson 8 | The sqlnet.ora file to define Network Connectivity Options |
| Objective | Describe the characteristics of the sqlnet.ora file for an Oracle server. |
Characteristics of the sqlnet.ora File for an Oracle Database 19c Shared Server
The
sqlnet.ora file is a configuration file used by Oracle Net Services to define network connectivity options and parameters for an Oracle Database. In an Oracle shared server configuration on 19c, the sqlnet.ora file plays a crucial role in configuring various network-related behaviors, including authentication methods, logging, tracing, and other communication-related settings. In shared server mode, where multiple clients share server processes via dispatchers, parameters related to connection timeouts, dead connection detection, and security are particularly important to ensure efficient resource management, prevent hanging sessions, and maintain secure, optimized performance across pooled connections.
Here are the key characteristics of the
sqlnet.ora file in a shared server configuration:
- Authentication Settings
- SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES: Specifies the authentication services to be used, such as
NONE,NTS(for Windows NT authentication), orKERBEROS5. In a shared server environment, this parameter determines how clients authenticate to the database, ensuring secure access across multiple shared processes.SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES = (NONE)
- SQLNET.ALLOWED_LOGON_VERSION_SERVER: Specifies the minimum authentication protocol version allowed for clients. This enhances security in shared server environments by restricting older, less secure protocol versions.
SQLNET.ALLOWED_LOGON_VERSION_SERVER = 12
- SQLNET.AUTHENTICATION_SERVICES: Specifies the authentication services to be used, such as
- Encryption and Integrity
- SQLNET.ENCRYPTION_SERVER: Defines whether encryption is required for client-server communication. In a shared server environment, this ensures secure communication between clients and shared server processes via dispatchers.
SQLNET.ENCRYPTION_SERVER = REQUIRED SQLNET.ENCRYPTION_TYPES_SERVER = (AES256)
- SQLNET.CRYPTO_CHECKSUM_SERVER: Configures message integrity (checksumming) between the client and server to prevent tampering during data transmission, vital for multi-user shared environments.
SQLNET.CRYPTO_CHECKSUM_SERVER = REQUIRED SQLNET.CRYPTO_CHECKSUM_TYPES_SERVER = (SHA256)
- SQLNET.ENCRYPTION_SERVER: Defines whether encryption is required for client-server communication. In a shared server environment, this ensures secure communication between clients and shared server processes via dispatchers.
- Logging and Tracing
- SQLNET.LOG_DIRECTORY_SERVER: Specifies the location where log files will be stored.
SQLNET.LOG_DIRECTORY_SERVER = $ORACLE_HOME/network/log
- SQLNET.LOG_FILE_SERVER: Sets the name of the log file for recording network events.
SQLNET.LOG_FILE_SERVER = sqlnet.log
- TRACE_LEVEL_SERVER: Defines the level of detail to be recorded in trace files (e.g.,
OFF,USER,ADMIN, orSUPPORT). These are helpful for diagnosing network issues in a shared server environment, where tracing can help identify dispatcher-related problems.TRACE_LEVEL_SERVER = ADMIN
- TRACE_DIRECTORY_SERVER: Specifies the directory for trace files.
TRACE_DIRECTORY_SERVER = $ORACLE_HOME/network/trace
- SQLNET.LOG_DIRECTORY_SERVER: Specifies the location where log files will be stored.
- Naming and Resolution
- NAMES.DIRECTORY_PATH: Specifies the naming methods to be used by Oracle Net Services for resolving network service names. Common methods include
TNSNAMES,LDAP, orEZCONNECT.NAMES.DIRECTORY_PATH = (TNSNAMES, EZCONNECT)
- NAMES.DIRECTORY_PATH: Specifies the naming methods to be used by Oracle Net Services for resolving network service names. Common methods include
- Connection Timeouts
- SQLNET.INBOUND_CONNECT_TIMEOUT: Defines the timeout period for inbound connections, ensuring that clients do not hang while trying to connect to the server. In shared servers, this helps manage dispatcher queues during high load.
SQLNET.INBOUND_CONNECT_TIMEOUT = 60
- TCP.CONNECT_TIMEOUT: Manages TCP connection timeouts between clients and the Oracle shared server.
TCP.CONNECT_TIMEOUT = 10
- SQLNET.INBOUND_CONNECT_TIMEOUT: Defines the timeout period for inbound connections, ensuring that clients do not hang while trying to connect to the server. In shared servers, this helps manage dispatcher queues during high load.
- Dead Connection Detection
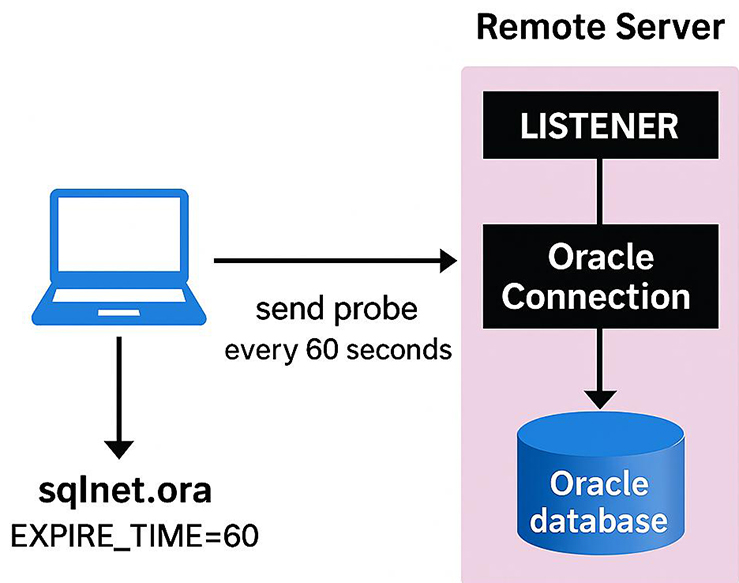
- SQLNET.EXPIRE_TIME: Specifies the time interval (in minutes) after which Oracle checks for a dead connection. This is especially crucial in shared server environments to clean up inactive sessions handled by dispatchers, freeing resources for other clients.
SQLNET.EXPIRE_TIME = 10
- SQLNET.EXPIRE_TIME: Specifies the time interval (in minutes) after which Oracle checks for a dead connection. This is especially crucial in shared server environments to clean up inactive sessions handled by dispatchers, freeing resources for other clients.
- Security
- SQLNET.WALLET_OVERRIDE: Determines whether to override the OS authentication with wallet credentials, enhancing security in shared setups.
SQLNET.WALLET_OVERRIDE = TRUE
- SQLNET.WALLET_OVERRIDE: Determines whether to override the OS authentication with wallet credentials, enhancing security in shared setups.
- Connection Management for Shared Servers
- USE_DEDICATED_SERVER: When set to
OFF, allows clients to use shared server connections if configured on the server side. Setting toONforces dedicated servers, overriding shared mode.USE_DEDICATED_SERVER = OFF
- In a shared server environment, connection load balancing and session multiplexing can be influenced by
sqlnet.orasettings, though primary configuration occurs in initialization parameters likeDISPATCHERS. Parameters here ensure clients route correctly to dispatchers for pooled resources.
- USE_DEDICATED_SERVER: When set to
sqlnet.ora file is an essential part of network configuration for Oracle databases in shared server mode, ensuring that all aspects of client-server communication are securely managed, authenticated, logged, and optimized for performance across shared processes.
Sample sqlnet.ora File Parameters
TRACE_LEVEL_SERVER = ADMIN
TRACE_DIRECTORY_SERVER = $ORACLE_HOME/network/trace
SQLNET.EXPIRE_TIME = 10
SQLNET.INBOUND_CONNECT_TIMEOUT = 60
NAMES.DEFAULT_DOMAIN = world
While most SQL*Net parameters are self-explanatory, key ones include:
- Trace levels (server) specify the amount of detail in trace files. Higher levels provide greater detail for troubleshooting dispatcher issues in shared servers.
- Directory locations direct where log and trace files are placed. If unspecified, defaults to
$ORACLE_HOME/network/logor$ORACLE_HOME/network/trace. - Expire time determines how often SQL*Net probes for active connections, critical in shared servers to terminate orphaned sessions and reclaim dispatcher resources.
The file
sqlnet.log records failed connection attempts. Oracle appends to this file indefinitely, so periodic cleanup is recommended. Below is a sample of a sqlnet.log file contents showing a listener-related error:
Fatal NI connect error 12541, connecting to: (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=TCP)(HOST=hostname)(PORT=1521))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=orcl)(CID=(PROGRAM=)(HOST=clienthost)(USER=oracle)))) VERSION INFORMATION: TNS for Linux: Version 19.0.0.0.0 - Production TCP/IP NT Protocol Adapter for Linux: Version 19.0.0.0.0 - Production Time: 06-AUG-2025 10:00:00 Tracing not turned on. Tns error struct: ns main err code: 12541 TNS-12541: TNS:no listener ns secondary err code: 12560 nt main err code: 511 TNS-00511: No listener nt secondary err code: 111 nt OS err code: 0
Key Error Codes:
- TNS-12541: TNS: no listener
- Indicates the Oracle listener is not running or unreachable, preventing connection routing in shared server setups.
- TNS-00511: No listener
- A network transport error showing the listener process is down or misconfigured.
- The error suggests the client cannot connect to the listener on the specified host and port (e.g., 1521). Resolve by verifying the listener status and configuration.
Fatal OSN Connect Error 12203 in Oracle Network Services
The Fatal OSN connect error 12203 (TNS-12203: TNS: unable to connect to destination) occurs when an Oracle client cannot establish a connection to the server, often due to issues in the Oracle Net Services layer. In shared server configurations, this can disrupt dispatcher handling. Specific Causes of OSN Connect Error 12203:- Listener Not Running:
- The Oracle Listener may not be running on the server.
- The client may be attempting to connect to the wrong listener.
- Incorrect or Missing listener.ora or tnsnames.ora Configuration:
- The tnsnames.ora file on the client might have incorrect connection details, such as the wrong host, port, or service name.
- The listener.ora file on the server could be misconfigured, preventing proper routing.
- Port or Firewall Issues:
- The connection port (commonly 1521) might be blocked by a firewall.
- The client could be trying to connect to a wrong or closed port.
- Network Issues:
- Network problems like DNS resolution failures or timeouts can prevent connections.
- The host specified may be unreachable.
- Version Mismatch:
- A mismatch between Oracle client and server versions can cause errors.
- Incorrect Service Name or SID:
- The service name or SID may not match the server configuration.
- Check Listener Status:
- Use the
lsnrctl statuscommand to verify the listener.
lsnrctl status - Use the
- Verify tnsnames.ora Configuration:
- Ensure correct details for host, port, and service name.
# Example entry in tnsnames.ora ORCL = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = your_server_host)(PORT = 1521)) (CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = your_service_name) ) ) - Verify Network Connectivity:
- Test with
pingortelnet.
ping your_server_host telnet your_server_host 1521 - Test with
- Check for Port Conflicts:
- Ensure the port is open and not in use by another process.
- Review Logs:
- Check the alert.log and listener log for errors.
ORA-12203: TNS:unable to connect to destination
Master Tnsnames.ora File - Exercise
Before moving on to the next lesson, click the Exercise link below to practice working with sqlnet.ora and tnsnames.ora files.
Master Tnsnames.ora File - Exercise
Master Tnsnames.ora File - Exercise