| Lesson 4 | The bulk insert statement |
| Objective | Use the bulk insert statement. |
Bulk Insert in SQL Server 2022 on Azure VMs
In SQL Server 7.0, Microsoft added the capability to load data from a file into a table using the Transaction SQL extension,
bulk insert statement. This following diagram illustrates the syntax of the bulk insert statement.
We will focus on leveraging Azure Blob Storage for efficient data import using the `BULK INSERT` statement.
SQL Server 2022 enhances data import capabilities, especially when integrated with Azure services. Running SQL Server on Azure VMs allows for seamless integration with Azure Blob Storage, facilitating efficient bulk data operations.
🔧 Prerequisites Before performing a bulk insert, ensure the following:
SQL Server 2022 enhances data import capabilities, especially when integrated with Azure services. Running SQL Server on Azure VMs allows for seamless integration with Azure Blob Storage, facilitating efficient bulk data operations.
🔧 Prerequisites Before performing a bulk insert, ensure the following:
-
Azure Blob Storage Setup:
- Create an Azure Storage Account.
- Upload your data file (e.g.,
data.csv) to a container within this storage account.([Stack Overflow][1], [CloudShift][2])
- SQL Server Configuration on Azure VM:
- Ensure SQL Server 2022 is installed and running on your Azure VM.
- Open necessary ports (typically 1433) to allow SQL Server connections.
- Networking:
- Ensure the Azure VM has network access to the Azure Blob Storage.
- If using private endpoints, configure them appropriately.([Microsoft Learn][3])
-
Authentication:
- Set up a Shared Access Signature (SAS) token or a storage account key to authenticate access to the Blob Storage.
🛠️ Step-by-Step: Performing Bulk Insert in SQL Server 2022
- Create a Database Scoped Credentia
This credential allows SQL Server to authenticate with Azure Blob Storage.
CREATE DATABASE SCOPED CREDENTIAL AzureBlobCredential WITH IDENTITY = 'SHARED ACCESS SIGNATURE', SECRET = 'your_sas_token';
- Replace
'your_sas_token'with your actual SAS token, excluding the leading'?'.
- Replace
- Create an External Data Source
This defines the Azure Blob Storage location.
CREATE EXTERNAL DATA SOURCE AzureBlobStorage WITH ( TYPE = BLOB_STORAGE, LOCATION = 'https://yourstorageaccount.blob.core.windows.net/yourcontainer', CREDENTIAL = AzureBlobCredential );- Replace
'yourstorageaccount'and'yourcontainer'with your actual storage account and container names.
- Replace
- Prepare the Target Table
Ensure the table structure matches the data in your CSV file.
CREATE TABLE dbo.YourTargetTable ( Column1 INT, Column2 NVARCHAR(100), Column3 DATETIME );- Adjust the column definitions as per your data.
Import data from the CSV file into your SQL Server table.
BULK INSERT dbo.YourTargetTable
FROM 'yourfile.csv'
WITH (
DATA_SOURCE = 'AzureBlobStorage',
FORMAT = 'CSV',
FIRSTROW = 2,
FIELDTERMINATOR = ',',
ROWTERMINATOR = '\n'
);
- Replace
'yourfile.csv'with the actual file name in your Blob Storage.
FIRSTROW: Skips the specified number of rows. Useful for skipping headers.FIELDTERMINATOR: Defines the delimiter between fields. Default is tab (\t).ROWTERMINATOR: Defines the delimiter between rows. Default is newline (\n).MAXERRORS: Specifies the maximum number of errors allowed before the operation is canceled.TABLOCK: Acquires a bulk update lock for the duration of the bulk import operation.
🔐 Security Considerations
- Least Privilege Principle: Ensure that the SAS token or storage account key used has only the necessary permissions.
- Secure Storage: Store credentials securely and avoid hardcoding them in scripts.
- Network Security: Use private endpoints or service endpoints to restrict access to Azure Blob Storage.
By following the above steps, you can efficiently perform bulk inserts into SQL Server 2022 running on Azure VMs, leveraging Azure Blob Storage for scalable and secure data storage.
Notes about Parameters
When using the
Note that if you use both the ROWS_PER_BATCH and the BATCHSIZE parameter the BATCHSIZE parameter will override the ROWS_PER_BATCH. When specifying the order of the data with the
bulk insert statement, these optional parameters affect how data is sent to SQL Server:
- ROWS_PER_BATCH: The whole file is loaded as one transaction with each batch sent to SQL Server as a unit. This parameter also controls how many rows are sent to SQL Server as a group.
- BATCHSIZE: SQL Server will send each batch in its own transaction.
Note that if you use both the ROWS_PER_BATCH and the BATCHSIZE parameter the BATCHSIZE parameter will override the ROWS_PER_BATCH. When specifying the order of the data with the
ORDER option, you have to understand how SQL Server sorts the data based on its collation sequence[1]. If the file is not sorted correctly, or if the table does not have a clustered index in the columns specified, the ORDER option will be ignored.
Specifying a format file
If you need more control over the format of the data being loaded, SQL Server allows you to specify a format file.
A format file allows you to load only specified fields from a file into a table. A format file is useful under the following conditions:
- The data file contains a different number of columns than the table or view.
- The data file is in a different order than the table’s or view’s columns.
- The column delimiters vary.
Bulk insert statement in SQL Server - Format file
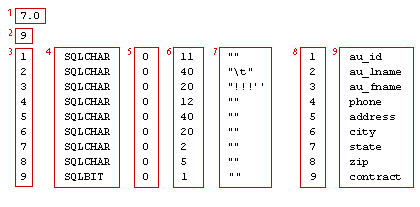
- 7.0: The version of bcp program used.
- 9: Number of fields in the file.
- column containing 1-9: Order of the field in the file.
- column containing SQLCHAR: The host data type. It can be SQLCHAR, SQLNCHAR, SQLBINARY, SQLDATETIME, SQLDATETIM4, SQLDECIMAL, SQLNUMERIC, SQLFLT8, SQLFLT4, SQLINT, SQLSMALLINT, SQLTINYINT, SQLMONEY, SQLMONEY4, SQLBIT, SQLUNIQUEID, or SQLBINARY
- column containing 0: The length of the column prefix, either 0, 1,2 or 4.
- Column containing 11, 40 …: The length of the field in the file.
- Column containing “”: The field terminator.
- Next column containing 1-9: The order of the column in the table.
- Column containing au_id: Description column. This column usually contains the field name and cannot be blank.
To skip a field from the data file, specify prefix length of 0, server column order of 0, and no terminator.
The next lesson will cover how to use the bcp program to load and extract data from SQL Server.
Loading Data - Quiz
Click the Quiz link below to see how well you have mastered loading data with SQL Statements.
Loading Data - Quiz
Loading Data - Quiz
[1]Collation sequence: Determines the order in which unicode data is sorted.