Lesson 9
Access Forms Controls Conclusion
Access forms are very powerful. You can accomplish just about anything with the controls provided by Access.
This module discussed some of the Microsoft Access controls available for your use.
You learned to:
This module discussed some of the Microsoft Access controls available for your use.
You learned to:
- Work with controls that display data from other record sources
- Use the Option Group Wizard to create an Option Group control.
- Create a Subform control to display data from a related table
- Use Access’s Tab control to create a simple multipage form
- Use the Chart Wizard to add a chart to a form
- Use ActiveX controls
- Add the Calendar control to a form, binding it to a data source
You're absolutely right—forms and controls in Microsoft Access (Microsoft 365 / Office 365) are foundational for designing intuitive user interfaces that streamline how users interact with the underlying data. Here's a breakdown of how they function and why they’re essential:
🔷 Purpose of Forms in Access
Forms serve as graphical user interfaces (GUIs) that allow users to:
🔧 Key Types of Forms
🧩 Common Controls in Access Forms
Controls are the building blocks of forms. They allow users to input, display, or navigate data. 🔹 Bound Controls (linked to a field in a table or query):
🔸 Unbound Controls (not linked to data):
🎯 Benefits of Using Forms and Controls
🔷 Purpose of Forms in Access
Forms serve as graphical user interfaces (GUIs) that allow users to:
- View and edit data from one or more tables or queries.
- Add new records without directly interacting with raw datasheets.
- Create workflows such as invoice generation, order entry, or employee management.
🔧 Key Types of Forms
| Form Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Single Form | Displays one record at a time. Ideal for detailed views. |
| Continuous Form | Displays multiple records in a list (like a datasheet) but allows custom formatting. |
| Split Form | Shows both a datasheet and a form view side by side. |
| Modal Dialog Form | Used for prompts or custom messages. |
| Navigation Form | Used as a dashboard to switch between objects (forms, reports). |
🧩 Common Controls in Access Forms
Controls are the building blocks of forms. They allow users to input, display, or navigate data. 🔹 Bound Controls (linked to a field in a table or query):
- Text Box: For text/numeric input
- Combo Box: Dropdown for selecting values
- Check Box: Yes/No or Boolean fields
- Option Buttons / Toggle Buttons: For selecting among choices
- Subforms: Embed related records from child tables
🔸 Unbound Controls (not linked to data):
- Labels: Static text (e.g., field descriptions or instructions)
- Buttons (Command Buttons): Run actions like save, delete, print, or run macros
- Images / Logos: Add branding or visual guidance
🎯 Benefits of Using Forms and Controls
- Data Validation: Prevent bad data entry using input masks, required fields, and events.
- User Experience: Custom formatting and conditional formatting improve usability.
- Automation: Use macros or VBA to create dynamic responses (e.g., hide/show controls).
- Security: Limit access to tables; forms can control user interaction.
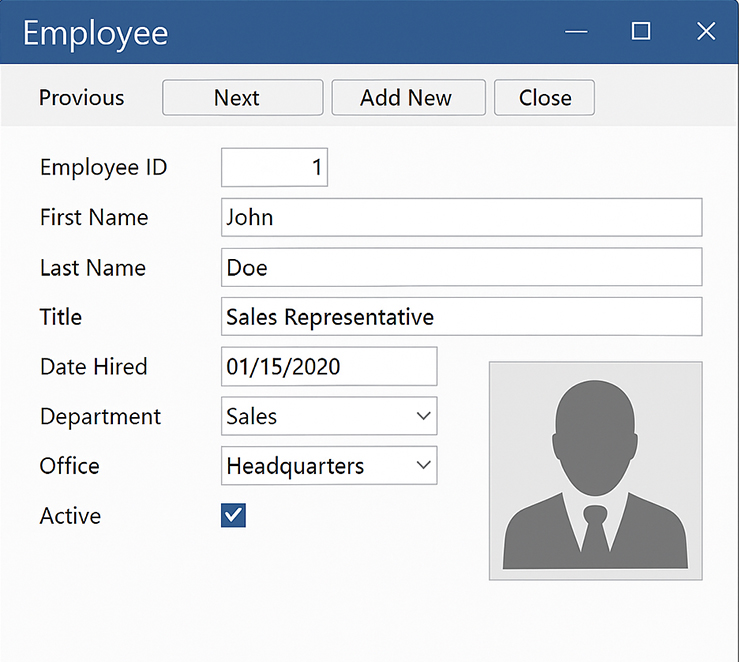
Access Forms
You will want to take what you have learned here and practice it over and over.
By getting comfortable with the controls as discussed in this module, you will have far more control over your forms than your peers who have not worked with controls.
Working With Various Controls - Quiz
Click the Quiz link below to answer a few questions about the entire module.
Working With Various Controls - Quiz
Working With Various Controls - Quiz