| Lesson 7 | The relational database management system |
| Objective | What are the functions of an RDBMS? |
Relational Database Management System
A database management system (DBMS) is software that controls the storage, organization, and retrieval of data.
Typically, a DBMS has the following elements:
A database application is a software program that interacts with a database to access and manipulate data. The first generation of database management systems included the following types:
Furthermore, the (DBMS) is a software interface that sits between a database and a user, or between a database and an application (such as an inventory system). Different DBMSs support different database models and different ways to create tables and perform CRUD operations.
- Kernel code: This code manages memory and storage for the DBMS.
- Repository of metadata: This repository is usually called a data dictionary.
- Query language: This language enables applications to access the data.
A database application is a software program that interacts with a database to access and manipulate data. The first generation of database management systems included the following types:
- Hierarchical: A hierarchical database organizes data in a tree structure. Each parent record has one or more child records, similar to the structure of a file system.
- Network: A network database is similar to a hierarchical database, except records have a many-to-many rather than a one-to-many relationship. The preceding database management systems stored data in rigid, predetermined relationships. Because no data definition language existed, changing the structure of the data was difficult and these systems lacked a simple query language, which hindered application development.
Furthermore, the (DBMS) is a software interface that sits between a database and a user, or between a database and an application (such as an inventory system). Different DBMSs support different database models and different ways to create tables and perform CRUD operations.
- DDLs [Data Definition Language] and
- DMLs [Data Manipulation Language].
Database Systems
Relational Database Management System (RDBMS)
A relational database management system (RDBMS) supports the relational model. It performs the same basic functions as those listed for a DBMS. SQL is the data definition and data manipulation language that is packaged with an RDBMS. The following series of images walks you through the major functions of a RDBMS.
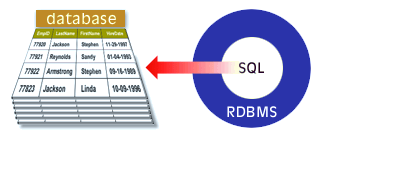
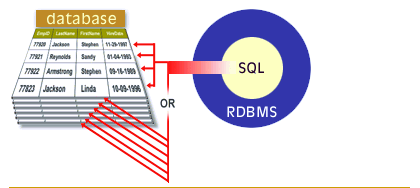
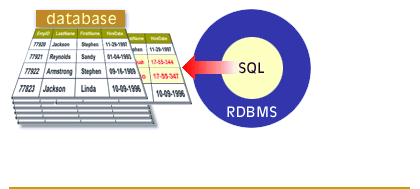
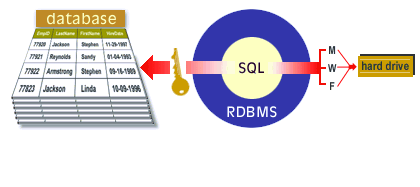
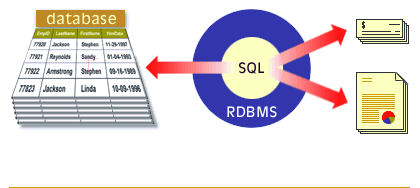
Functions of RDBMS
A (RDBMS) relational database management system is a term used to describe an entire suite of programs for both
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) serves as a cornerstone in the field of data management and storage. It operates on the premise of the relational model, introduced by E.F. Codd, which organizes data into tables (relations) consisting of rows and columns. The fundamental functions of an RDBMS encompass several key aspects:
In summary, a Relational Database Management System provides a comprehensive framework for storing, retrieving, securing, and managing data in a structured format, offering robust tools for ensuring data integrity, security, and performance.
- managing a relational database and
- communicating with that relational database engine.
A Relational Database Management System (RDBMS) serves as a cornerstone in the field of data management and storage. It operates on the premise of the relational model, introduced by E.F. Codd, which organizes data into tables (relations) consisting of rows and columns. The fundamental functions of an RDBMS encompass several key aspects:
- Data Storage, Retrieval, and Update: At its core, an RDBMS efficiently stores data in a structured format, using tables. It allows for the retrieval of data through queries, typically written in SQL (Structured Query Language). Users can insert, update, delete, and query data, managing both data and relationships between data.
- Data Integrity and Accuracy: The RDBMS enforces data integrity rules to maintain the accuracy and reliability of data. This includes constraints like primary keys (unique identifiers for each record), foreign keys (which establish relationships between tables), and check constraints (which ensure that data entered into a database meets specific criteria).
- Data Security: It provides mechanisms to control access to data. This includes authentication (verifying who is accessing the database) and authorization (determining what they are allowed to do). The RDBMS can restrict access to specific tables, fields, or rows within a table.
- Data Backup and Recovery: The RDBMS also includes tools for backing up data and recovering data in the event of a failure. This ensures that data is not lost and can be restored to a consistent state.
- Transaction Management: It supports transactions, which are sequences of operations performed as a single logical unit of work. Each transaction is atomic, consistent, isolated, and durable (ACID properties). This means that transactions are processed reliably and ensure the integrity of the database.
- Concurrent Access and Locking Mechanisms: An RDBMS allows multiple users to access and modify the database concurrently. It employs locking mechanisms and other strategies to ensure that concurrent access does not affect the integrity of the data.
- Query Processing and Optimization: The RDBMS includes a query processor to interpret and execute SQL queries. It employs various optimization techniques to ensure that queries are executed in the most efficient manner possible.
- Scalability and Performance: It is designed to scale in response to increased data volume or user load, maintaining performance levels. This includes capabilities like clustering, partitioning, and replication.
- Data Abstraction and Independence: The RDBMS provides a level of abstraction between the physical storage of data and the logical view presented to users. This data independence allows changes to be made to the database's physical storage without affecting how users access it.
- Support for Advanced Features: Modern RDBMSs support advanced features like stored procedures, triggers, and views, which allow for more complex operations and data manipulations.
In summary, a Relational Database Management System provides a comprehensive framework for storing, retrieving, securing, and managing data in a structured format, offering robust tools for ensuring data integrity, security, and performance.
Providing Data Abstraction and Application flexibility with Relational Databases
Relational databases were originally proposed to separate the physical storage of data from its conceptual representation and to provide a mathematical foundation for data representation and querying. The relational data model also introduced a "high-level query language" (SQL) that provided an alternative to programming language interfaces, making it much faster to write new queries. Relational systems were initially targeted to the same applications as earlier systems and provided flexibility
Early experimental relational systems developed in the late 1970s and the commercial relational database management systems (RDBMS) introduced in the early 1980s were quite slow, since they did not use physical storage pointers or record placement to access related data records.With the development of new storage and indexing techniques and better query processing and optimization, their performance improved. Eventually, relational databases became the dominant type of database system for traditional database applications.
- to develop new queries quickly and
- to reorganize the database as requirements changed.
Early experimental relational systems developed in the late 1970s and the commercial relational database management systems (RDBMS) introduced in the early 1980s were quite slow, since they did not use physical storage pointers or record placement to access related data records.With the development of new storage and indexing techniques and better query processing and optimization, their performance improved. Eventually, relational databases became the dominant type of database system for traditional database applications.
RDBMS Management and Functions
One RDBMS can manage many relational databases. Oracle, Microsoft, IBM, MySQL, and Sybase have comprehensive RDBMSs available on the market. Each company packages its product(s) with utilities to enhance RDBMS capabilities and performance. Product prices vary widely among these top competitors.

A Database Management System (DBMS) is a software tool designed to efficiently manage, organize, and interact with databases. The primary functions of a DBMS include:
These functions make DBMS essential for managing large-scale data in modern applications, ensuring data reliability, security, and efficiency in various industries.
The next lesson discusses the concept of database change management.
-
Data Storage, Retrieval, and Management
- Storage: Allows data to be stored systematically, ensuring efficient use of disk space.
- Retrieval: Provides tools and query languages (e.g., SQL) to fetch data quickly based on specific conditions.
- Management: Facilitates the addition, modification, and deletion of data while maintaining its structure and integrity.
-
Data Integrity and Consistency
- Ensures that the data entered into the database adheres to predefined rules and constraints.
- Prevents inconsistent or invalid data through mechanisms such as primary keys, foreign keys, and data validation.
-
Data Security
- Protects data from unauthorized access or malicious attacks using user authentication, role-based access control, and encryption.
- Logs user activities for auditing purposes.
-
Transaction Management
- Ensures that all database transactions follow the ACID properties (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and Durability) to guarantee data accuracy and reliability.
- Provides rollback and commit functionalities to handle failures during transactions.
-
Concurrency Control
- Manages simultaneous data access by multiple users or applications, ensuring that transactions do not interfere with each other.
- Implements locking mechanisms to prevent data corruption during concurrent access.
-
Backup and Recovery
- Provides tools for creating data backups to protect against data loss.
- Facilitates recovery mechanisms to restore the database to a consistent state after hardware failures, software errors, or unexpected interruptions.
-
Data Abstraction
- Separates the physical storage of data from the logical view presented to users.
- Supports multiple levels of abstraction (physical, logical, and external) to simplify data access for different types of users.
-
Query Processing
- Parses and executes user queries written in query languages like SQL.
- Optimizes queries to enhance performance and reduce resource consumption.
-
Data Sharing
- Allows multiple users and applications to access and use the database simultaneously while maintaining data integrity.
- Ensures consistency across shared data in distributed systems.
-
Metadata Management
- Maintains a data dictionary or catalog that stores information about the database structure, schemas, and relationships between data.
- Provides tools for schema definition, modification, and management.
-
Performance Monitoring and Tuning
- Monitors database performance to identify bottlenecks.
- Offers tools to optimize database operations, such as indexing, query optimization, and caching.
-
Support for Multi-User Environments
- Coordinates access to the database among multiple users or applications, avoiding conflicts and ensuring fair resource allocation.
These functions make DBMS essential for managing large-scale data in modern applications, ensuring data reliability, security, and efficiency in various industries.
The next lesson discusses the concept of database change management.
RDBMS - Exercise
Before moving on to the next lesson, click the Exercise link below to check your knowledge of the functions of an RDBMS.
RDBMS - Exercise
RDBMS - Exercise
[1]Data abstraction: Data abstraction is the reduction of a particular body of data to a simplified representation of the whole.
[2]Data Independence: Data Independence is defined as a property of DBMS that helps you to change the Database schema at one level of a database system without requiring to change the schema at the next higher level.